TR1 Manual
Edit this on GitLab
TR1 Measurement & Simulation Modules Thermocouple and RTD Measurement
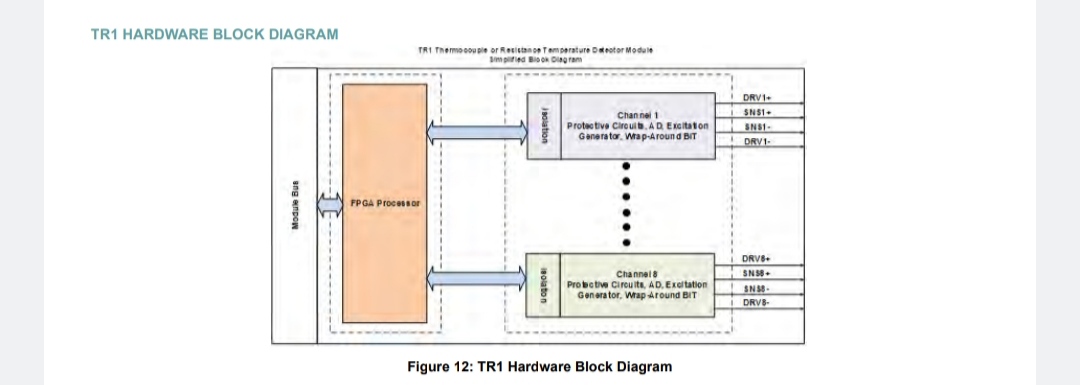
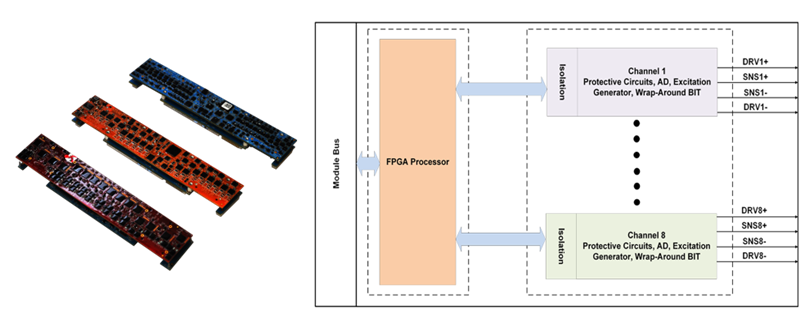
The TR1 provides 8 channels which can be individually programmed as a Thermocouple (TC) or a Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) measurement interface. When configured as a TC, the channel can interface with virtually all thermocouple-type NIST temperature ranges. When configured as an RTD, the channel can interface to two, three and four-wire platinum RTD sensor configurations. The TR1 channels are individually configurable for up to 8 isolated TC or low-voltage range A/D measurement channels. Configuration programmability provides interfaces for industry standard NIST thermocouple types (J, K, T, E, N, B, R, and S). The TR1 channels are individually configurable for up to 8 isolated RTD measurement channels. Each channel is configurable for use with 4-wire, 3- wire or 2-wire connections to the RTD sensors. All RTD channels provide measurement results in Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) format.
FEATURES
-
Thermocouple Measurement
-
Interfaces with most standard NIST thermocouple types (J, K, T, E, N, B, R, and S)
-
Self-powered
-
Large temperature range; up to 2300° C
-
Accuracy up to ±0.2° C (thermocouple type dependent)
-
Thermo-block compensation option P/N ACC-ISO-THERM-BLK2 (If accessory used, channel 8 is automatically allocated as an RTD interface for the thermo-block compensation temperature measurement)
-
-
RTD Measurement
-
Higher accuracy and repeatability as compared with thermocouples in applications below 600 °C
-
Two, three or four-wire mode
-
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) format
-
Open sensor connections are detected and reported
-
1 mA, 500 µA, 250 µA & 100 µA excitation sources for Pt100, Pt500, Pt1000 and Pt2000 ranges
-
-
Independently Programmable
-
Up to 8 RTD channels
-
Up to 8 Thermocouple channels
-
-
Independent Mode Select
-
Configures Thermocouple or RTD
-
-
Programmable Sample Rate
-
Sets the sampling rate of the A/D
-
-
Offset Temperature
-
Provides ability to null for any system induced measurement errors
-
SPECIFICATIONS
Thermocouple
A/D Converter |
Independent 24-bit Sigma-Delta type (one for each channel) |
Temperature Range |
NIST temperature range (J, K, T, E, N, B, R, S thermocouple types) |
Voltage Measurement Range |
±78.125 mV to an accuracy of ± 25 µV over operational temperature. |
Overvoltage Input Tolerance |
± 4 V continuous, ±50 V momentary duration limited to 100 ms (applied at signal input) |
50/60 Hz Noise Rejection |
>70 dB |
CMR |
85 dB (minimum) |
Differential Input Impedance |
>10 KΩ |
Digital Output |
IEEE 754-2008 (binary32) programmable for ° C, ° F (programmed for temperature), 24-bit (signed), based on % FSR (±78 mV) (programmed for A/D) |
Accuracy |
Based on minimum update rate and w/thermocouple block I/F compensation; ±0.2° C (Type J/N), ±0.3° C (Type K), ±0.3° C (Type T/E), ±0.3° C (Type R/S), ±0.9° C (Type B), ± 0.2% FSR (programmed for raw A/D digital output) Resolution 0.01° typ. (programmed for temperature, thermocouple selection dependent) |
Sample Rate |
Programmable between 3-4800 Hz |
Thermo-Block Interface |
Optional thermocouple interface for connection of up to 7 thermocouple sensors. Pt100 RTD sensor for cold junction compensation temperature. |
Build-In-Test (BIT) |
Continuous background ‘online' accuracy, OPEN detection capability. |
RTD
Analog Input Resolution |
24 bits per channel |
RTD Interface |
4, 3, or 2-wire RTD interface capability. Specifically designed for use with common 100 Ω, 500 Ω, 1000 Ω and 2000 Ω RTDs with general resistance measurement capability up to 8000 Ω. Direct readout of temperature in ° C / ° F with standard Pt sensors. |
Open Line Detection |
Ability to detect an open in any line or RTD in all wire modes. |
Excitation |
1mA (Pt100), 500µA (Pt500), 250µA (Pt1000) or 100µA (Pt2000) for 2- & 4-wire mode; 500µA (Pt100), 250µA (Pt500), 125µA (Pt1000) or 50µA (Pt2000) for 3-wire mode |
Accuracy |
±0.1% of full-scale value @ 5 samples per second (4-wire mode only), ±0.2% of full-scale value @ 5samples per second (3-wire mode only), ±1.2% of full-scale value @ 5 samples per second (2-wire mode only) |
Sample Rate |
Programmable between 3-4800 Hz |
Output Format |
Resistance/Temperature |
Built-In-Test (BIT) |
Continuous background 'online' accuracy, OPEN detection capability. |
General
Power |
+5 VDC @ 480 mA typ. |
Ground |
Independent channels; isolated from system ground. |
Weight |
1.5 oz. (42 g) |
ESD Protection |
Designed to meet the testing requirements of IEC 801-2 Level 2. (4 kV transient with a peak current of 7.5 A and a Tc of approximately 60 ns) |
Number of Channels |
Eight channels programmable for RTD or Thermocouple mode. |
Input Interface |
Independent differential input channels. |
Architected for Versatility
Edit this on GitLab
NAI’s Configurable Open Systems Architecture™ (COSA®) offers a choice of over 100 smart I/O, communications, or Ethernet switch functions, providing the highest packaging density and greatest flexibility of ruggedized embedded product solutions in the industry. Preexisting, fully-tested functions can be combined in an unlimited number of ways quickly and easily.
One-Source Efficiencies
Eliminate man-months of integration with a configured, field-proven system from NAI. Specification to deployment is a seamless experience as all design, state-of-the-art manufacturing, assembly and test are performed - by one trusted source. All facilities are located within the U.S. and optimized for high-mix/low volume production runs and extended lifecycle support.
Product Lifecycle Management
From design to production and beyond, NAI’s product lifecycle management strategy ensures the long-term availability of COTS products through configuration management, technology refresh and obsolescence component purchase and storage.
INTRODUCTION
As a leading manufacturer of smart function modules, NAI offers over 100 different modules that cover a wide range of I/O, measurement and simulation, communications, Ethernet switch, and SBC functions. Our TR1 smart function module provides 8 channels which can be individually configured as a Thermocouple (TC) or Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) measurement interface. This user manual is designed to help you get the most out of our Thermocouple/RTD smart function module.
TR1 Overview
NAI’s TR1 module offers a range of advanced features tailored to meet the demands of precision measurement applications, both in Thermocouple mode and RTD mode, including the following:
Thermocouple Features
NIST Thermocouple Interface Capability: In thermocouple mode, the TR1 module features configuration programmability which provides interfaces for all standard NIST thermocouple types (J, K, T, E, N, B, R, and S), providing unparalleled versatility in thermocouple compatibility.
Self-Powered: One standout feature of the thermocouple mode is its self-powered functionality, eliminating the need for external power sources and simplifying installation. This not only streamlines the setup process but also enhances its suitability for a wide range of applications.
Large Temperature Range: The thermocouple function boasts an expansive temperature measurement range, reaching a remarkable 2300⁰C. This exceptional range makes it well-suited for applications where extreme temperatures are encountered, such as jet engines and gas turbine exhaust.
Up to ±0.2⁰C Accuracy: With thermo-block compensation, the thermocouple provides compensated measurements at accuracies up to ±0.2⁰C.
Optional Thermo-Block Compensation: NAI offers an optional accessory (ACC-ISO-THERM-BLK2) which connects to the thermocouple sensors, allowing for automatic cold junction compensation temperature through an onboard RTD temperature sensor (CH8 will automatically configure to RTD mode if this accessory is used).
RTD Features
Higher Accuracy and Repeatability: The TR1’s RTD mode excels in accuracy and repeatability when compared to thermocouples, making it an ideal choice for applications with operating temperatures below 600°C. This characteristic ensures that critical measurements are obtained with the utmost precision.
Wire Modes: The module provides flexibility with two, three, or four-wire modes, allowing users to adapt to various measurement setups and requirements, enhancing versatility in different scenarios.
Data Format: The TR1 module utilizes the Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) format for data representation, enabling compatibility and ease of integration with other systems and equipment.
Open Sensor Detection: When configured for RTD mode, the TR1 module is equipped with a built-in feature to detect and report open sensor connections. This safeguards against inaccurate measurements caused by sensor failures, promoting data integrity.
Excitation Sources: To accommodate various RTD ranges when configured for RTD mode, the TR1 provides excitation sources of 1 mA (Pt100), 500 μA (Pt500), 250 μA (Pt1000), and 100 μA (Pt2000) for 2- & 4-wire modes, and 500 μA (Pt100), 250 μA (Pt500), 125 μA (Pt1000), and 50 μA (Pt2000) for 3-wire mode. This feature ensures precise measurements across a wide range of applications.
General Features
Independently Programmable: The TR1 module offers the capability to independently program up to 8 RTD or Thermocouple channels. This feature is invaluable for engineers working on complex systems with multiple measurement points, allowing for tailored configuration and control.
Programmable Sample Rate: Users can set the sampling rate of the analog-to-digital converter (A/D) to match the specific needs of their application. This programmable sample rate ensures that data acquisition is optimized for accuracy and efficiency.
Offset Temperature: The offset temperature feature provides users with the means to nullify system-induced measurement errors. This is crucial in achieving the highest level of measurement precision and reliability, especially in critical applications where accuracy is paramount.
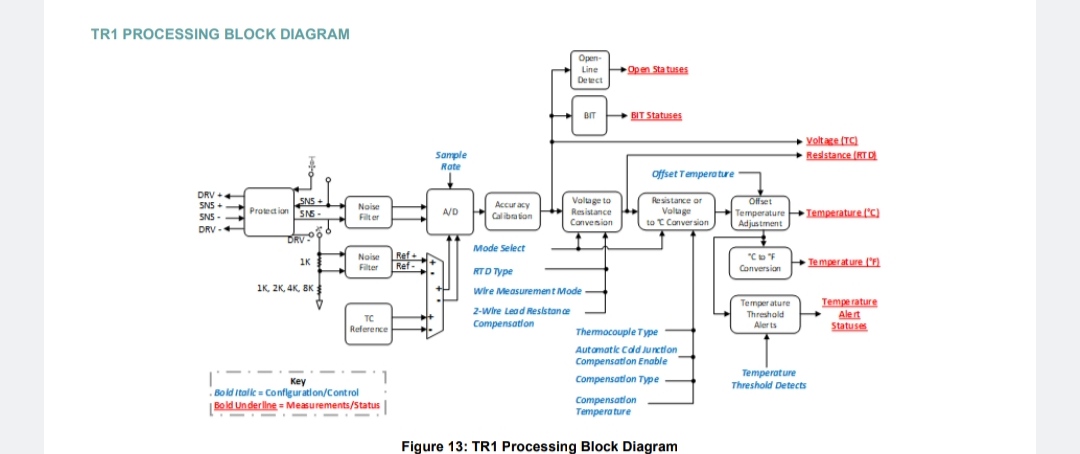
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
The TR1 is programmable for either Thermocouple or RTD measurement via the Mode Select register.
Thermocouple Capability
While in thermocouple mode, the TR1 provides up to eight individual isolated thermocouple or low-voltage range A/D measurement channels. Configuration programmability provides interfaces for industry standard NIST thermocouple types (J, K, T, E, N, B, R, and S).
Thermocouples are widely used temperature-measurement devices because of their ruggedness, repeatability and fast response time. They offer a cost-effective means for measuring a much wider range of temperatures in comparison to other common solutions like resistance temperature devices (RTD), thermistors, or temperature-sensing integrated circuits (ICs). Although thermocouples can be used over a wider range of temperatures than RTDs and temperature-sensing ICs, they are far less linear. Also, RTDs and temperature-sensing ICs typically offer better sensitivity and accuracy. Thermocouple signals are very low-level and often require amplification or a high-resolution data converter to process the signals. Despite these disadvantages, overall cost, ease of use, and wide temperature range make thermocouples popular.
Thermocouples are constructed with two wires made from dissimilar metals. One wire is predesignated as the positive side, and the other as the negative. The industry standard NIST thermocouple types are defined by the metals or alloys used and the temperature range allowed for each type. Each thermocouple type offers a unique thermoelectric characteristic over its specified temperature range.
In Figure 1, the voltage generated by the loop is a function of the temperature difference between the two junctions. This phenomenon is known as the Seebeck effect which is described as the process in which thermal energy is converted into electrical energy. The Peltier effect is the opposite of the Seebeck effect which is the process of converting electrical energy to thermal energy. In Figure 1, the measure output voltage (V ) is a function of the difference between the measuring (hot) junction voltage and the reference (cold) junction voltage. Since V and V are generated by a temperature difference between the two junctions, V is also a function of this temperature difference. The scale factor, α (Seebeck coefficient), relates the voltage difference to the temperature difference.
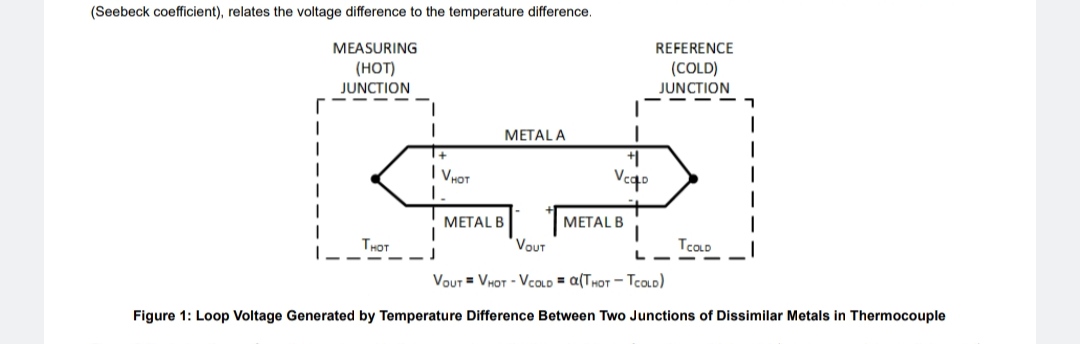
Figure 1. Loop Voltage Generated by Temperature Difference Between Two Junctions of Dissimilar Metals in Thermocouple
Figure 2 illustrates the configuration most commonly used in thermocouple applications. In this configuration, a third metal (known as an intermediate metal) such as copper, is introduced into the loop and the two additional junctions. In this configuration, provided the two junctions are at the same temperature, the intermediate metal type has no effect on the output voltage. This configuration allows the thermocouple to be used without a separate reference junction. V is still a function of the difference between the hot- and cold-junction temperature, related by the Seebeck coefficient. In this configuration, the cold-junction temperature must be known in order to determine the actual temperature measured at the hot-junction.
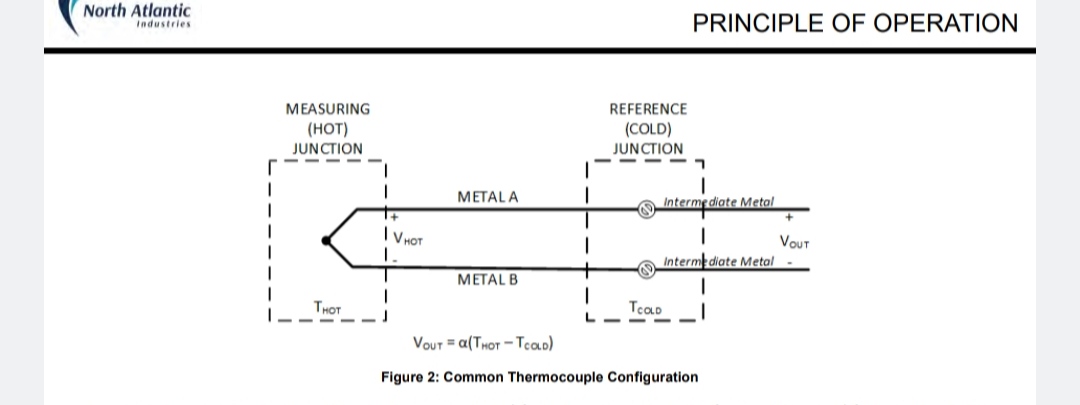
Figure 2: Common Thermocouple Configuration
The simplest case occurs when the cold-junction temperature is at 0° C, also known as an ice-bath reference. At T = 0° C, V = V. In this case, the voltage measured at the hot-junction is a direct translation of the actual temperature at that junction.
When the cold-junction temperature is not at 0° C, the temperature of this junction must be known in order to determine the actual hot-junction temperature. The output voltage of the thermocouple must also be compensated to account for the voltage created by the nonzero cold-junction temperature. This process is known as cold-junction compensation.
NAI provides an optional accessory, NAI P/N ACC-ISO-THERM-BLK2, a thermocouple connection interface comprised of a separate isothermal interface/terminal block. The thermocouple sensors are connected to the accessory’s copper measurement wiring harness, allowing for automatic cold junction compensation temperature through an onboard RTD temperature sensor reporting the terminal temperature to a dedicated channel on the module (refer to Appendix A: Optional External Cold Junction Compensation Block Accessory).
|
Note
|
when the configuration for the isothermal interface/terminal block (referred to as Cold Junction Compensation Block) is selected, Channel 8 of the TR1 module will be automatically configured for RTD mode, so this channel cannot be used as a thermocouple channel. |
In lieu of the External Cold Junction Compensation Block Accessory, a user supplied terminal connection block may also be used, provided the terminal temperature is measured and maintained in the manual cold junction compensation temperature register for proper compensation. A benefit of this would be the availability of Channel 8 for an additional Thermocouple or RTD measurement channel.
In addition to cold-junction temperature compensation, the TR1 provides the ability to program temperature offsets, which can be used to null out small temperature deviations from sensors or system interconnections as well as delta measurements from an initial temperature reading. The offset temperature is subtracted from the output temperature reading and may be configured individually for each channel.
The fundamental design of the TR1 is based on independent 24-bit Sigma-Delta A/D converters for each channel. This allows the TR1 to also be used for direct precision low voltage measurements (±78.125 mV) for uses in low-voltage range A/D applications (i.e. shunt resistor voltage/current sense measurements).
TR1 is designed for rugged embedded “on-the-move” or laboratory-grade environments, and provides continuous background built-in-test (BIT) capabilities for accuracy and “open” detection monitoring and flagging.
RTD Capability
The TR1 channels are individually configurable for up to 8 RTD measurement channels. Each channel is configurable for use with 4-wire, 3-wire or 2-wire connections to the RTD sensors. All RTD channels are calibrated at the factory and measurement results provided in Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) format.
Open sensor connections are detected and reported in an Open status word. A 1mA excitation source is used for resistance measurement in the lowest range setting (Pt100). For the Pt500, Pt1000 and Pt2000 ranges, the excitation current sources are 500µA, 250µA, and 100µA respectively.
Lead resistance correction is available in 2-wire mode, allowing for user compensation of cabling resistance in the measurement system. Resistance values may be entered for individual channels, which are subtracted from the measurement. The temperature measurements will reflect the compensated resistance values for the RTD for direct readout of the corrected temperature readings.
As with the Thermocouple mode, the temperature offset provisions allow for the same nulling of the temperature offsets in the system and operate similarly.
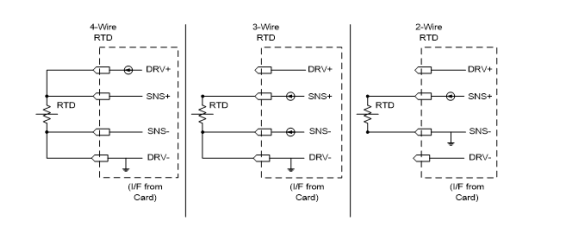
2-Wire is the simplest resistance measurement configuration, requiring only two wires per sensor. Measurements will be very sensitive to test cabling, as the excitation current and voltage measurements are through the same wires. Short or low resistance test leads are needed for accurate readings. Provisions for nulling the test lead resistances are provided via individual 2-wire offset resistance registers, allowing direct readings of the compensated measurements on a per channel basis.
3-Wire configuration relies on balanced test lead resistance on the Sense (+) and Sense (-) wires, so the voltage drop across each of the two current source lines are equal and cancel each other out. The differential voltage reading between the two sense lines along with the excitation current through the resistor is used in the resulting calculation of the sensor resistance. The test lead wire length will not affect the measurement provided the two lines are equal in resistance and is often the best compromise between wiring requirements and accuracy. In 3-Wire mode, the excitation current is split in half. Half of the total current flows on each of the sense lines (see 3-Wire RTD connection diagram).
4-Wire configuration provides optimal accuracy, allowing precise measurements without any constraints of short or balanced test leads, but requires 4 wires per sensor. The two sense wires measure the voltage at the sensor independently without undue influence of voltage drops due to the excitation current. This configuration is recommended where accuracy is a priority over the additional wiring requirements.
Low Voltage A/D Measurement Capability
The module can measure low voltage dynamic signals in the microvolt range with faster update rates to 4800 Hz. Readings can track dynamic signals when high rates are selected, with some increase in noise jitter. Optimal accuracy and reading stability will be achieved by low update rate selections.
Default configuration runs periodic maintenance in the background for self-test and calibration at 30 second intervals, which briefly suspends reading updates during the performance of these routines. For time critical measurements, the periodic internal processes may optionally be suspended for continuous and uninterrupted readings. During this time, these maintenance operations may be triggered manually by the user at suitable intervals.
Automatic Background Built-In Test (BIT)/Diagnostic Capability
Automatic background BIT testing is provided. Each channel is checked at periodic intervals for correct A/D operation using an internal measurement of an on-board resistor reference. The open input detection test applies a low-level current pulse to the A/D converter inputs and tests for a full-scale 3.3V limit, indicating an open sensor circuit. Any failure triggers an interrupt if enabled, with the results available in the status registers. The testing is transparent to the user and has no effect on the operation of this module. Enabled by default at power on, it may optionally be disabled.
Temperature Threshold Detect Programming
The TR1 provides the ability to program two temperature thresholds that will result in temperature alerts. For each threshold, a “low” and a “high” threshold value is specified that will be used to set the Temperature Alert statuses. The Temperature Threshold Low registers sets the threshold values to use to set the Temperature Alert Low status bit when the Temperature reading is below the low temperature threshold value. Conversely, the Temperature Threshold High registers sets the threshold values to use to set the Temperature Alert High status bit when the Temperature reading is above the high temperature threshold value. These threshold values are individually configurable on a per channel basis. A possible usage of the two temperature thresholds is to use the first threshold detection levels as an early warning pre-alarm level and the second threshold detection levels as an alarm limit value. For this purpose, the Detect 2 thresholds should be set at larger deviation values from the nominal temperature than the Detect 1 thresholds.
For example:
[Threshold Low 2] < [Threshold Low 1] < [Nominal Temperature] < [Threshold High 1] < [Threshold High 2]
This allows the Detect 1 thresholds to serve as a pre-alert warning of temperature excursion, while Detect 2 may represent an alarm condition.
|
Note
|
these detect thresholds are not necessarily set in this order and may be independently set either way. |
Status and Interrupts
The TR1 Function Module provide registers that indicate faults or events. Refer to “Status and Interrupts Module Manual” for the Principle of Operation description.
Module Common Registers
The TR1 Function Module includes module common registers that provide access to module-level bare metal/FPGA revisions & compile times, unique serial number information, and temperature/voltage/current monitoring. Refer to “Module Common Registers Module Manual” for the detailed information.
REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
The register descriptions provide the Register Name, Type, Data Range, Read or Write information, power on default initialized values, a description of the function and a data table where applicable,
TR1 Measurement Registers
The TR1 measurement registers provide Temperature measurements (in both Celsius and Fahrenheit degrees), for RTD mode, Resistance measurements, and for Thermocouple mode, Voltage measurements.
Temperature (°C)
Function: |
Measures the temperature of the thermocouple/ RTD sensor. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
RTD/Thermocouple temperature measurement in degrees Celsius. For Thermocouple, the measurement values will be dependent upon the appropriate selections made in the Thermocouple Type and Compensation Type registers. |
Temperature (°F)
Function: |
Measures the temperature of the thermocouple/ RTD sensor. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
RTD/Thermocouple temperature measurement in degrees Fahrenheit. For Thermocouple, the value is dependent upon the appropriate and expected selections made in the Thermocouple Type and Compensation Type registers. |
Thermocouple - Specific Measurement Registers
When the TR1 module channel is configured for Thermocouple mode, in addition to the temperature measurements, the Voltage measurement is also available.
Voltage
Function: |
Measures the direct input voltages at the TR1 channels. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
Voltage measurement of the TR1 channel in V. |
NOTE: the register does not include the cold junction compensation.
RTD - Specific Measurement Registers
When the TR1 module channel is configured for RTD mode, in addition to the temperature measurements, the Resistance measurement is also available.
Resistance
Function: |
Measures resistance of the RTD sensor. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
Measures resistance in ohms. This measurement may optionally be adjusted through a user entry of a 2-wire lead resistance compensation value. |
TR1 Control Registers
The TR1 control registers provide the ability to configure the channels to either Thermocouple or RTD mode and specifying the sample rate. For Thermocouple channels, the configuration requirements include specification of the Thermocouple type and Thermocouple temperature compensation settings. For RTD channels, configuration requirements include specifying the RTD type, the RTD wire-measurement mode and resistance compensation (resistance compensation is only required for channels configured in 2-Wire mode).
Mode Select
Function: |
Configures the TR1 channel to either Thermocouple or RTD mode. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0xFF, bitmapped per channel (All channels in RTD Mode) |
Operational Settings: |
Configures the channel for Thermocouple (0) or RTD (1) mode. |
NOTE: for if Automatic Cold Junction Compensation Enable register is enabled, Channel 8 will automatically be configured in RTD mode.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
Ch8 - configured automatically to RTD mode, if Automatic Cold Junction Compensation Enable = 1
Sample Rate
Function: |
Sets the sampling rate of the sensor. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x00 to 0x27 (See table) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0x27 (3 Hz) |
Operational Settings: |
Set the value based on Sample Rate table. Note: lower rates provide greater stability and accuracy in the readings. Per channel configuration. |
Sample Rate Register Value |
Update Frequency (Hz) |
0x0 |
4800 |
0x1 |
2400 |
0x2 |
1600 |
0x3 |
1200 |
0x4 |
960 |
0x5 |
800 |
0x6 |
600 |
0x7 |
480 |
0x8 |
400 |
0x9 |
320 |
0xA |
300 |
0xB |
240 |
0xC |
200 |
0xD |
192 |
0xE |
160 |
0xF |
150 |
0x10 |
120 |
0x11 |
100 |
0x12 |
96 |
0x13 |
80 |
0x14 |
75 |
0x15 |
64 |
0x16 |
60 |
0x17 |
50 |
0x18 |
48 |
0x19 |
40 |
0x1A |
32 |
0x1B |
30 |
0x1C |
25 |
0x1D |
24 |
0x1E |
20 |
0x1F |
16 |
0x20 |
15 |
0x21 |
12 |
0x23 |
8 |
0x24 |
6 |
0x25 |
5 |
0x26 |
4 |
0x27 |
3 |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Offset Temperature
Function: |
Set a user defined offset temperature in °C. The value in this register is subtracted from the temperature readings. The raw voltage and resistance readings are not affected. Programming the Offset Temperature register provides the ability to null any system measurement errors and adjust slight variations in the thermocouple and measurement circuitry. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0.0 |
Operational Settings: |
Sets the user defined offset temperature to be used. |
Thermocouple - Specific Control
For TR1 module channels configured in Thermocouple mode, additional configurations and controls include the Thermocouple Type, Automatic Cold Junction Compensation Enable, the Compensation Type, and the Compensation Temperature.
For time critical measurements, such as using a channel for low voltage A/D measurements, the TR1 module provides registers to suspend the maintenance operations which briefly suspends the updates of measurement readings.
Thermocouple Type
Function: |
Sets the type of thermocouple (J, K, T, E, N, B, R, S) |
Type: |
ASCII Hex as unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
See table. |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
'K' (0x4B) (Default set on channel configuration switch from RTD to Thermocouple mode) |
Operational Settings: |
Set the Thermocouple Type as specified in the table. |
NOTE: the register entry is the ASCII hex equivalent value for the thermocouple type.
Thermocouple Type |
ASCII Entry (Hex Conversion) |
J |
0x4A |
K |
0x4B |
T |
0x54 |
E |
0x45 |
N |
0x4E |
B |
0x42 |
R |
0x52 |
S |
0x53 |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Automatic Cold Junction Compensation Enable
Function: |
When Automatic Cold Junction Compensation is enabled, Channel 8 is automatically configured in RTD mode, to allow its temperature reading to be used for compensation of terminal connection temperatures at other than 0 deg C. NOTE: the RTD temperature reading for Channel 8 will be used as the Thermocouple Compensation Temperature only for channels with the Compensation Type set to “automatic compensation”; otherwise the manual temperature compensation entries for those channels will still apply. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0 or 1 |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
Enable (1) or disable (0) to use the RTD reading for Channel 8 as the Compensation Temperature when Compensation Type is set to “automatic compensation”. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D |
Compensation Type
Function: |
Selects the compensation value source to use for the Thermocouple Temperature value. The selection can either be the user specified value in the Compensation Temperature register or the Channel 8 RTD reading from the accessory Cold Junction Compensation Block. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0 (user specified temperature) or 1 (use Ch.8 temperature reading) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0x0 (manual) |
Operational Settings: |
Set to user defined selection (0) to use the value in the Compensation Temperature register. Set to automatic compensation (1) to use Channel 8 RTD reading from the Cold Junction Compensation Block. |
|
Note
|
when the Compensation Type for any channel is set to automatic compensation (1), the Automatic Cold Junction Compensation Enable register should be enabled (1) as well to ensure channel 8 properly compensates the Thermocouple Temperature readings. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D |
Compensation Temperature
Function: |
Set a user defined compensation temperature in °C. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0.0 (NOTE: Value is reset to default whenever channel configuration is toggled between Thermocouple and RTD mode.) |
Operational Settings: |
Sets the user defined compensation temperature to be used. |
Suspend Background Maintenance Operations Register
The default configuration of the module is to run periodic self-test and calibration at 30 second intervals. During these operations, updates to the measurement readings are briefly suspended. For time critical measurements, such as using a channel for low voltage A/D measurements, the periodic internal processes may optionally be suspended for continuous and uninterrupted readings. During this suspended time, the maintenance operations for calibration and open-line detect may be triggered manually by the application at suitable intervals.
Suspend Background Maintenance Operations
Function: |
Holds off the performance of periodic maintenance routines for internal system calibration (TC mode), open line status checking, and built in test (BIT). Used for dynamic measurements for continuous reading updates without interruption from the brief maintenance operations. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 (All channels run maintenance operations on a scheduled basis) |
Operational Settings: |
Suspends periodic operations for open line status check, system calibration, and BIT. Set to 0 to perform periodic operations for channel (default). Set bit to 1 to suspend the background maintenance operations for the specified channel. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
Run System Calibration
Function: |
Triggers performance of internal system calibration for channels where the periodic maintenance operations have been disabled. The calibration is normally run at 2 minute intervals to compensate for any internal drift on measurements. This one-time trigger is only used when the periodic schedule has been disabled for time critical measurements. This allows the user to run the routine in between measurement sessions. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
Write a 1 to the corresponding bit for the channel. Bit is self-clearing and will reset to zero on completion of the routine. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
Run Open-Line Check
Function: |
Triggers check for open or unconnected channels to update the open status indication. This is only used when the periodic schedule has been disabled for time critical measurements. This allows the application to run the routine in between measurement sessions. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
Write a 1 to the corresponding bit for the channel. Bit is self-clearing and will reset to zero on completion of the routine. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
Run BIT
Function: |
Triggers Built-In-Test to detect out of tolerance conditions on the measurement circuitry. Only used when the periodic schedule for the channel has been disabled for time critical measurements. This allows the user to run the routine in between measurement sessions. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
Write a 1 to the corresponding bit for the channel. Bit is self-clearing and will reset to zero on completion of the routine. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
RTD - Specific Control
For TR1 module channels configured in RTD mode, additional configurations and controls include the RTD Type, Wire Measurement Mode and 2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation
RTD Type
Function: |
RTD nominal resistance at 0°C. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
See table |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
100.0 (0x42C8 0000 in floating point) |
Operational Settings: |
Set the RTD Type as specified in the table. |
RTD Type |
Description |
Pt100 |
0-100 Ω RTD; resistance range of 0 Ω to approximately 500 Ω |
Pt500 |
0-500 Ω RTD; resistance range of 0 Ω to approximately 2000 Ω |
Pt1000 |
0-1000 Ω.RTD; resistance range of 0 Ω to approximately 4000 Ω |
Pt2000 |
0-2000 Ω.RTD; resistance range of 0 Ω to approximately 8000 Ω |
Wire Measurement Mode
Function: |
Sets the RTD sensor configuration: 2, 3 or 4 wire. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
2 - 4 |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
2 (Value is set to 2-wire default whenever channel configuration mode is changed to RTD. |
Operational Settings: |
Set the Wire Measurement Mode as specified in the table. |
Wire Measurement Mode Value |
Description |
2 |
2-wire configuration |
3 |
3-wire configuration |
4 |
4-wire configuration |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D |
D |
D |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation
Function: |
Set a user defined compensation resistance in ohms, primarily required for channels that are configured for 2-wire configuration in the Wire Measurement Mode register. This allows test lead or cabling resistances to be cancelled out when using a 2-wire configuration. The Resistance measurement reading is adjusted by subtracting the value set in this register to null test lead and cabling resistance. This resistance offset is also applied in 3- and 4-wire modes, though typically not required in those modes. NOTE: the applied offsets will also affect the corresponding temperature readings as the adjusted resistance values are used for the internal calculation of temperature for the RTD sensors. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0.0 |
Operational Settings: |
Set the TOTAL lead resistance to be subtracted from the resistance measurement and reported in the Resistance register. |
Temperature Threshold Detect Programming
The TR1 Temperature Threshold registers provide the ability program two temperature thresholds that will result in temperature alerts.
Temperature Threshold Detect 1
A “low” and a “high” threshold value is specified for each temperature threshold that will be used to set the Temperature Alert statuses. The Temperature Threshold Low 1 register sets the threshold value to use to set the Temperature Alert Low 1 status bit when the Temperature reading is below the low temperature threshold value. Conversely, the Temperature Threshold High 1 register sets the threshold values to use to set the Temperature Alert High 1 status bit when the Temperature reading is above the high temperature threshold value. These threshold values are individually configurable on a per channel basis.
Temperature Threshold Low 1
Function: |
Sets Temperature Threshold Low 1 value in degrees Celsius for each channel. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
-40° C |
Operational Settings: |
If the temperature drops below this set value, then a Temperature Alert Low 1 Status will be set. An interrupt will occur if the Temperature Alert Low 1 Interrupt Enable register is set to 1. |
Temperature Threshold High 1
Function: |
Sets Temperature Threshold High 1 value in degrees Celsius for each channel. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
25° C |
Operational Settings: |
If the temperature exceeds the set value, then a Temperature Alert High 1 Status will be set. An interrupt will occur if the Temperature Alert High 1 Interrupt Enable register is set to 1. |
Temperature Threshold Detect 2
A “low” and a “high” threshold value is specified for each temperature threshold that will be used to set the Temperature Alert statuses. The Temperature Threshold Low 2 register sets the threshold value to use to set the Temperature Alert Low 2 status bit when the Temperature reading is below the low temperature threshold value. Conversely, the Temperature Threshold High 2 register sets the threshold values to use to set the Temperature Alert High 2 status bit when the Temperature reading is above the high temperature threshold value. These threshold values are individually configurable on a per channel basis.
Temperature Threshold Low 2
Function: |
Sets Temperature Threshold Low 2 value in degrees Celsius for each channel. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0°C |
Operational Settings: |
If the temperature drops below the set value, then a Temperature Alert Low 2 Status will be set. An interrupt will occur if the Temperature Alert Low 2 Interrupt Enable register is set to 1. |
Temperature Threshold High 2
Function: |
Sets Alert Temperature High 2 value in degrees Celsius for each channel. |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
100° C |
Operational Settings: |
If the temperature exceeds the set value, then a Temperature Alert High 2 Status will be set. An interrupt will occur if the Temperature Alert High 2 Interrupt Enable register is set to 1. |
Module Common Registers
Refer to “Module Common Registers Module Manual” for the register descriptions.
Status and Interrupt Registers
The TR1 Module provides status registers for BIT, Open, and Temperature Alert.
Channel Status Enabled
Function: |
Determines whether to update the status for the channels. This feature can be used to “mask” status bits of unused channels in status registers that are bitmapped by channel. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF (Channel Status) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0x0000 00FF |
Operational Settings: |
When the bit corresponding to a given channel in the Channel Status Enabled register is not enabled (0) the status will be masked and report “0” or “no failure”. This applies to all statuses that are bitmapped by channel (BIT Status, Open Status, Temperature Alerts and Summary Status). |
|
Note
|
Background BIT will continue to run even if the Channel Status Enabled is set to 0. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
BIT Status
There are four registers associated with the BIT Status: Dynamic, Latched, Interrupt Enable, and Set Edge/Level Interrupt.
Function: |
Indicates the corresponding channels associated with the channel’s BIT status or configuration |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R (Dynamic), R/W (Latched, Interrupt Enable, Edge/Level Interrupt) |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
BIT Dynamic Status |
|||||||||||||||
BIT Latched Status |
|||||||||||||||
BIT Interrupt Enable |
|||||||||||||||
BIT Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
Open Status
There are four registers associated with the Open Status: Dynamic, Latched, Interrupt Enable, and Set Edge/Level Interrupt.
Function: |
Sets the corresponding bit associated with the channel’s Open status indication for an unconnected input. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R (Dynamic), R/W (Latched, Interrupt Enable, Edge/Level Interrupt) |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Open Dynamic Status |
|||||||||||||||
Open Latched Status |
|||||||||||||||
Open Interrupt Enable |
|||||||||||||||
Open Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
Temperature Alert Status
There are four registers associated with each of the Temperature Alert Statuses: Dynamic, Latched, Interrupt Enable, and Set Edge/Level Interrupt.
Function: |
Sets the corresponding bit associated with the channel’s Temperature Alert indication for temperature readings that are below or above the associated thresholds. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R (Dynamic), R/W (Latched, Interrupt Enable, Edge/Level Interrupt) |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Temperature Alert Low 1 Dynamic Status |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert Low 1 Latched Status |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert Low 1 Interrupt Enable |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert Low 1 Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert High 1 Dynamic Status |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert High 1 Latched Status |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert High 1 Interrupt Enable |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert High 1 Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert Low 2 Dynamic Status |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert Low 2 Latched Status |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert Low 2 Interrupt Enable |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert Low 2 Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert High 2 Dynamic Status |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert High 2 Latched Status |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert High 2 Interrupt Enable |
|||||||||||||||
Temperature Alert High 1 Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
Summary Status
There are four registers associated with the Summary Status: Dynamic, Latched, Interrupt Enable, and Set Edge/Level Interrupt.
Function: |
Sets the corresponding bit when a fault is detected for BIT or Open on that channel. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R (Dynamic), R/W (Latched, Interrupt Enable, Edge/Level Interrupt) |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Summary Status Dynamic Status |
|||||||||||||||
Summary Status Latched Status |
|||||||||||||||
Summary Status Interrupt Enable |
|||||||||||||||
Summary Status Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ch8 |
Ch7 |
Ch6 |
Ch5 |
Ch4 |
Ch3 |
Ch2 |
Ch1 |
Interrupt Vector and Steering
When interrupts are enabled, the interrupt vector associated with the specific interrupt can be programmed (typically with a unique number/identifier) such that it can be utilized in the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) to identify the type of interrupt. When an interrupt occurs, the contents of the Interrupt Vector registers is reported as part of the interrupt mechanism.
In addition to specifying the interrupt vector, the interrupt can be directed (“steered”) to the native bus or to the application running on the onboard ARM processor.
|
Note
|
The Interrupt Vector and Interrupt Steering registers are mapped to the Motherboard Common Memory and these registers are associated with the Module Slot position (refer to Function Register Map). |
Interrupt Vector
Function: |
Set an identifier for the interrupt. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
When an interrupt occurs, this value is reported as part of the interrupt mechanism. |
Interrupt Steering
Function: |
Sets where to direct the interrupt. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
See table |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
When an interrupt occurs, the interrupt is sent as specified: |
Direct Interrupt to VME |
1 |
Direct Interrupt to ARM Processor (via SerDes) (Custom App on ARM or NAI Ethernet Listener App) |
2 |
Direct Interrupt to PCIe Bus |
5 |
Direct Interrupt to cPCI Bus |
6 |
FUNCTION REGISTER MAP
Key:
Bold Italic |
= Configuration/Control |
Bold Underline |
= Measurement/Status |
*When an event is detected, the bit associated with the event is set in this register and will remain set until the user clears the event bit. Clearing the bit requires writing a 1 back to the specific bit that was set when read (i.e. write-1-to-clear, writing a '1' to a bit set to '1' will set the bit to '0').
~ Data is always in Floating Point.
TR1 Measurement Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1004 |
Temperature (ºC) Ch 1~ |
R |
0x1044 |
Temperature (ºC) Ch 2~ |
R |
0x1084 |
Temperature (ºC) Ch 3~ |
R |
0x10C4 |
Temperature (ºC) Ch 4~ |
R |
0x1104 |
Temperature (ºC) Ch 5~ |
R |
0x1144 |
Temperature (ºC) Ch 6~ |
R |
0x1184 |
Temperature (ºC) Ch 7~ |
R |
0x11C4 |
Temperature (ºC) Ch 8~ |
R |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1008 |
Temperature (ºF) Ch 1~ |
R |
0x1048 |
Temperature (ºF) Ch 2~ |
R |
0x1088 |
Temperature (ºF) Ch 3~ |
R |
0x10C8 |
Temperature (ºF) Ch 4~ |
R |
0x1108 |
Temperature (ºF) Ch 5~ |
R |
0x1148 |
Temperature (ºF) Ch 6~ |
R |
0x1188 |
Temperature (ºF) Ch 7~ |
R |
0x11C8 |
Temperature (ºF) Ch 8~ |
R |
Thermocouple-Specific Measurement Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1000 |
Voltage Ch 1~ |
R |
0x1040 |
Voltage Ch 2~ |
R |
0x1080 |
Voltage Ch 3~ |
R |
0x10C0 |
Voltage Ch 4~ |
R |
0x1100 |
Voltage Ch 5~ |
R |
0x1140 |
Voltage Ch 6~ |
R |
0x1180 |
Voltage Ch 7~ |
R |
0x11C0 |
Voltage Ch 8~ |
R |
RTD-Specific Measurement Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1000 |
Resistance Ch 1~ |
R |
0x1040 |
Resistance Ch 2~ |
R |
0x1080 |
Resistance Ch 3~ |
R |
0x10C0 |
Resistance Ch 4~ |
R |
0x1100 |
Resistance Ch 5~ |
R |
0x1140 |
Resistance Ch 6~ |
R |
0x1180 |
Resistance Ch 7~ |
R |
0x11C0 |
Resistance Ch 8~ |
R |
TR1 Control Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x2000 |
Mode Select Ch 1-8 |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1028 |
Sample Rate Ch 1 |
R/W |
0x1068 |
Sample Rate Ch 2 |
R/W |
0x10A8 |
Sample Rate Ch 3 |
R/W |
0x10E8 |
Sample Rate Ch 4 |
R/W |
0x1128 |
Sample Rate Ch 5 |
R/W |
0x1168 |
Sample Rate Ch 6 |
R/W |
0x11A8 |
Sample Rate Ch 7 |
R/W |
0x11E8 |
Sample Rate Ch 8 |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x102C |
Offset Temperature Ch 1~ |
R/W |
0x106C |
Offset Temperature Ch 2~ |
R/W |
0x10AC |
Offset Temperature Ch 3~ |
R/W |
0x10EC |
Offset Temperature Ch 4~ |
R/W |
0x112C |
Offset Temperature Ch 5~ |
R/W |
0x116C |
Offset Temperature Ch 6~ |
R/W |
0x11AC |
Offset Temperature Ch 7~ |
R/W |
0x11EC |
Offset Temperature Ch 8~ |
R/W |
Thermocouple-Specific Control Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x100C |
Thermocouple Type Ch 1 |
R/W |
0x104C |
Thermocouple Type Ch 2 |
R/W |
0x108C |
Thermocouple Type Ch 3 |
R/W |
0x10CC |
Thermocouple Type Ch 4 |
R/W |
0x110C |
Thermocouple Type Ch 5 |
R/W |
0x114C |
Thermocouple Type Ch 6 |
R/W |
0x118C |
Thermocouple Type Ch 7 |
R/W |
0x11CC |
Thermocouple Type Ch 8 |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x2004 |
Automatic Cold Junction Compensation Enable |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1010 |
Compensation Type Ch 1 |
R/W |
0x1050 |
Compensation Type Ch 2 |
R/W |
0x1090 |
Compensation Type Ch 3 |
R/W |
0x10D0 |
Compensation Type Ch 4 |
R/W |
0x1110 |
Compensation Type Ch 5 |
R/W |
0x1150 |
Compensation Type Ch 6 |
R/W |
0x1190 |
Compensation Type Ch 7 |
R/W |
0x11D0 |
Compensation Type Ch 8 |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1014 |
Compensation Temperature Ch 1~ |
R/W |
0x1054 |
Compensation Temperature Ch 2~ |
R/W |
0x1094 |
Compensation Temperature Ch 3~ |
R/W |
0x10D4 |
Compensation Temperature Ch 4~ |
R/W |
0x1114 |
Compensation Temperature Ch 5~ |
R/W |
0x1154 |
Compensation Temperature Ch 6~ |
R/W |
0x1194 |
Compensation Temperature Ch 7~ |
R/W |
0x11D4 |
Compensation Temperature Ch 8~ |
R/W |
Thermocouple-Specific Suspend Maintenance Operations Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x2008 |
Suspend Background Operations |
R/W |
0x200C |
Run System Calibration |
R/W |
0x2010 |
Run Open-Line Check |
R/W |
0x2014 |
Run BIT |
R/W |
RTD-Specific Control Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x100C |
RTD Type Ch 1 |
R/W |
0x104C |
RTD Type Ch 2 |
R/W |
0x108C |
RTD Type Ch 3 |
R/W |
0x10CC |
RTD Type Ch 4 |
R/W |
0x110C |
RTD Type Ch 5 |
R/W |
0x114C |
RTD Type Ch 6 |
R/W |
0x118C |
RTD Type Ch 7 |
R/W |
0x11CC |
RTD Type Ch 8 |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1010 |
Wire Measurement Mode Ch 1 |
R/W |
0x1050 |
Wire Measurement Mode Ch 2 |
R/W |
0x1090 |
Wire Measurement Mode Ch 3 |
R/W |
0x10D0 |
Wire Measurement Mode Ch 4 |
R/W |
0x1110 |
Wire Measurement Mode Ch 5 |
R/W |
0x1150 |
Wire Measurement Mode Ch 6 |
R/W |
0x1190 |
Wire Measurement Mode Ch 7 |
R/W |
0x11D0 |
Wire Measurement Mode Ch 8 |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1014 |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation Ch 1~ |
R/W |
0x1054 |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation Ch 2~ |
R/W |
0x1094 |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation Ch 3~ |
R/W |
0x10D4 |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation Ch 4~ |
R/W |
0x1114 |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation Ch 5~ |
R/W |
0x1154 |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation Ch 6~ |
R/W |
0x1194 |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation Ch 7~ |
R/W |
0x11D4 |
2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation Ch 8~ |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x2008 |
Suspend Background Operations |
R/W |
0x2010 |
Run Open-Line Check |
R/W |
0x2014 |
Run BIT |
R/W |
Temperature Threshold Detect Programming Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1018 |
Air Temperature Low 1 Ch 1~ |
R/W |
0x1058 |
Air Temperature Low 1 Ch 2~ |
R/W |
0x1098 |
Air Temperature Low 1 Ch 3~ |
R/W |
0x10D8 |
Air Temperature Low 1 Ch 4~ |
R/W |
0x1118 |
Air Temperature Low 1 Ch 5~ |
R/W |
0x1158 |
Air Temperature Low 1 Ch 6~ |
R/W |
0x1198 |
Air Temperature Low 1 Ch 7~ |
R/W |
0x11D8 |
Air Temperature Low 1 Ch 8~ |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x101C |
Air Temperature Low 2 Ch 1~ |
R/W |
0x105C |
Air Temperature Low 2 Ch 2~ |
R/W |
0x109C |
Air Temperature Low 2 Ch 3~ |
R/W |
0x10DC |
Air Temperature Low 2 Ch 4~ |
R/W |
0x111C |
Air Temperature Low 2 Ch 5~ |
R/W |
0x115C |
Air Temperature Low 2 Ch 6~ |
R/W |
0x119C |
Air Temperature Low 2 Ch 7~ |
R/W |
0x11DC |
Air Temperature Low 2 Ch 8~ |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1020 |
Air Temperature High 1 Ch 1~ |
R/W |
0x1060 |
Air Temperature High 1 Ch 2~ |
R/W |
0x10A0 |
Air Temperature High 1 Ch 3~ |
R/W |
0x10E0 |
Air Temperature High 1 Ch 4~ |
R/W |
0x1120 |
Air Temperature High 1 Ch 5~ |
R/W |
0x1160 |
Air Temperature High 1 Ch 6~ |
R/W |
0x11A0 |
Air Temperature High 1 Ch 7~ |
R/W |
0x11E0 |
Air Temperature High 1 Ch 8~ |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1024 |
Air Temperature High 2 Ch 1~ |
R/W |
0x1064 |
Air Temperature High 2 Ch 2~ |
R/W |
0x10A4 |
Air Temperature High 2 Ch 3~ |
R/W |
0x10E4 |
Air Temperature High 2 Ch 4~ |
R/W |
0x1124 |
Air Temperature High 2 Ch 5~ |
R/W |
0x1164 |
Air Temperature High 2 Ch 6~ |
R/W |
0x11A4 |
Air Temperature High 2 Ch 7~ |
R/W |
0x11E4 |
Air Temperature High 2 Ch 8~ |
R/W |
Module Common Registers
Refer to “Module Common Registers Module Manual” for the Module Common Registers Function Register Map.
Status Registers
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x02B0 |
Channel Status Enabled |
R/W |
BIT Status
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0800 |
Dynamic Status |
R |
0x0804 |
Latched Status* |
R/W |
0x0808 |
Interrupt Enable |
R/W |
0x080C |
Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
R/W |
Open
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0810 |
Dynamic Status |
R |
0x0814 |
Latched Status* |
R/W |
0x0818 |
Interrupt Enable |
R/W |
0x081C |
Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
R/W |
Temperature Alert Low 1
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0820 |
Dynamic Status |
R |
0x0824 |
Latched Status* |
R/W |
0x0828 |
Interrupt Enable |
R/W |
0x082C |
Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
R/W |
Temperature Alert Low 2
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0830 |
Dynamic Status |
R |
0x0834 |
Latched Status* |
R/W |
0x0838 |
Interrupt Enable |
R/W |
0x083C |
Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
R/W |
Temperature Alert High 1
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0840 |
Dynamic Status |
R |
0x0844 |
Latched Status* |
R/W |
0x0848 |
Interrupt Enable |
R/W |
0x084C |
Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
R/W |
Temperature Alert High 2
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0850 |
Dynamic Status |
R |
0x0854 |
Latched Status* |
R/W |
0x0858 |
Interrupt Enable |
R/W |
0x085C |
Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
R/W |
Summary Status
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x09A0 |
Dynamic Status |
R |
0x09A4 |
Latched Status* |
R/W |
0x09A8 |
Interrupt Enable |
R/W |
0x09AC |
Set Edge/Level Interrupt |
R/W |
Interrupt Registers
The Interrupt Vector and Interrupt Steering registers are located on the Motherboard Memory Space and do not require any Module Address Offsets. These registers are accessed using the absolute addresses listed in the table below.
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0500 |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0504 |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0508 |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x050C |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0510 |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0514 |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0518 to 0x0564 |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0568 |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x056C to 0x057C |
Module 1 Interrupt Vector 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0600 |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0604 |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0608 |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x060C |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0610 |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0614 |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0618 to 0x0664 |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0668 |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x066C to 0x067C |
Module 1 Interrupt Steering 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0700 |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0704 |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0708 |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x070C |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0710 |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0714 |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0718 to 0x0764 |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0768 |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x076C to 0x077C |
Module 2 Interrupt Vector 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0800 |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0804 |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0808 |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x080C |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0810 |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0814 |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0818 to 0x0864 |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0868 |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x086C to 0x087C |
Module 2 Interrupt Steering 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0900 |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0904 |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0908 |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x090C |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0910 |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0914 |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0918 to 0x0964 |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0968 |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x096C to 0x097C |
Module 3 Interrupt Vector 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0A00 |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0A04 |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0A08 |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x0A0C |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0A10 |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0A14 |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0A18 to 0x0A64 |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0A68 |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x0A6C to 0x0A7C |
Module 3 Interrupt Steering 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0B00 |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0B04 |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0B08 |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x0B0C |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0B10 |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0B14 |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0B18 to 0x0B64 |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0B68 |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x0B6C to 0x0B7C |
Module 4 Interrupt Vector 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0C00 |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0C04 |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0C08_* |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x0C0C |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0C10 |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0C14 |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0C18 to 0x0C64 |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0C68 |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x0C6C to 0x0C7C |
Module 4 Interrupt Steering 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0D00 |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0D04 |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0D08 |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x0D0C |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0D10 |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0D14 |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0D18 to 0x0D64 |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0D68 |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x0D6C to 0x0D7C |
Module 5 Interrupt Vector 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0E00 |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0E04 |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0E08 |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x0E0C |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0E10 |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0E14 |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0E18 to 0x0E64 |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0E68 |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x0E6C to 0x0E7C |
Module 5 Interrupt Steering 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x0F00 |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x0F04 |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x0F08 |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x0F0C |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x0F10 |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x0F14 |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x0F18 to 0x0F64 |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x0F68 |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x0F6C to 0x0F7C |
Module 6 Interrupt Vector 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
Addr (Hex) |
Name |
Read/Write |
0x1000 |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 1 - BIT |
R/W |
0x1004 |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 2 - Open |
R/W |
0x1008 |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 3 - Temperature Alert Low 1 |
R/W |
0x100C |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 4 - Temperature Alert Low 2 |
R/W |
0x1010 |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 5 - Temperature Alert High 1 |
R/W |
0x1014 |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 6 - Temperature Alert High 2 |
R/W |
0x1018 to 0x1064 |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 7-26 - Reserved |
R/W |
0x1068 |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 27 - Summary |
R/W |
0x106C to 0x107C |
Module 6 Interrupt Steering 28-32 - Reserved |
R/W |
APPENDIX A: OPTIONAL EXTERNAL COLD JUNCTION COMPENSATION (CJC) BLOCK ACCESSORY
Thermocouple applications require an interface from the base motherboard/module to the thermocouple wires, providing a transition from the thermocouple wires to conventional (copper) wiring for the measurement. Conventional wiring (copper), when connected to the thermocouple wire, will create a junction of dissimilar metals. When a junction of dissimilar metals occurs at temperatures other than a standard 0.0 deg C, there will be an additional voltage gradient developed, acting as an additional thermocouple and affecting the reading of the primary thermocouple. Compensation is required for this temperature delta offset. The effect of the junction temperature needs to be factored into the measurement to provide the correct readings. The effects of the temperature reading on the measurement is not a direct arithmetic correction due to the nonlinear response characteristics of thermocouples. The compensation calculations involve the thermocouple type and the temperature measurement points.
The primary purpose of the isothermal block is to provide a consistent temperature environment for the terminal blocks connecting thermocouple wires to the system interface to the motherboard/module and provides the measurement of the junction temperature. This allows the cold junction compensation temperature to be done automatically. The isothermal block contains an RTD temperature sensor and is constructed to minimize temperature variances between channels and the isothermal block itself. The sensor is read by a designated RTD channel (Ch.8) to allow automatic compensation with the junction temperature measurement.
The NAI P/N ACC-ISO-THERM-BLK2 is a semi-rugged, non-sealed housing designed with terminals to secure up to 7 thermocouple interconnects (one for each available channel of the TR1). It is designed to be mounted/secured to a “cold plate” (surface/mass that is expected to maintain a relatively stable and constant temperature over time). The isothermal block has an embedded Pt100 RTD temperature sensor for measurement of the junction temperature. The TR1 module, when programmed for external block compensation mode, will utilize this reference temperature reading and provide automatic thermocouple measurement compensation based on the temperature reading of the sensor.

Figure 3. NAI ACC-ISO-THERM-BLK2
ACC-ISO-THERM-BLK2 Detail Summary, Mechanical & Electrical
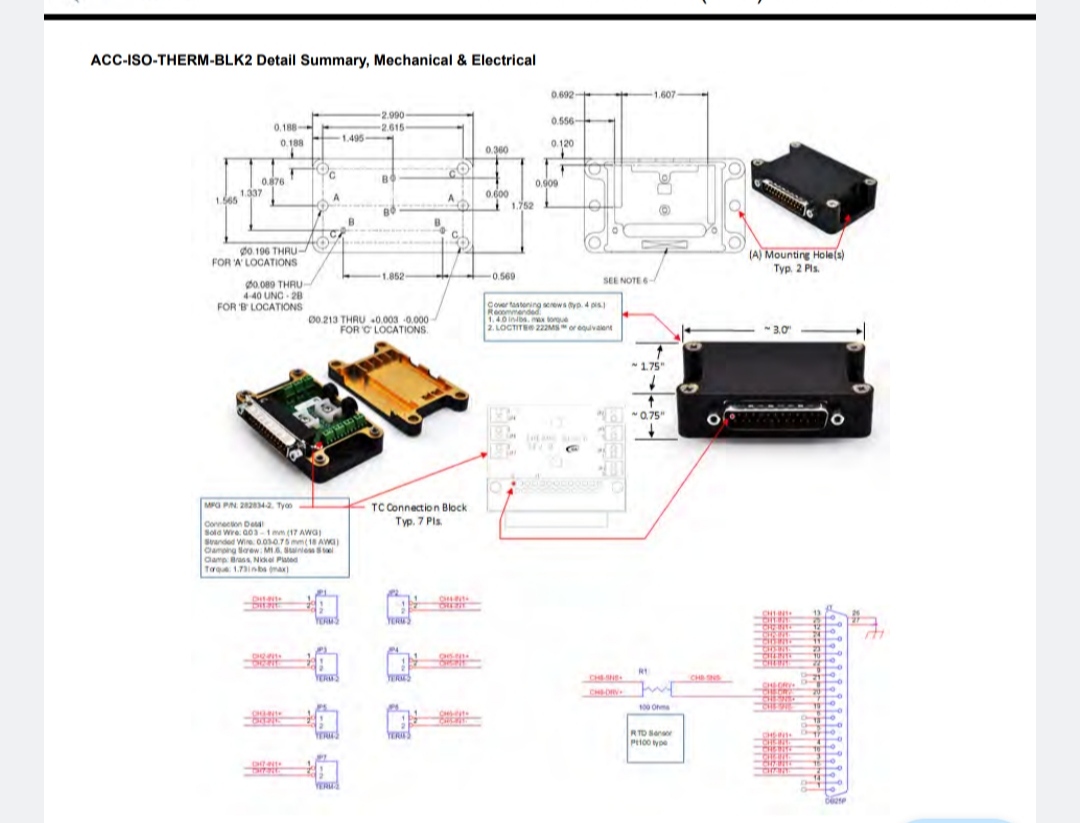
APPENDIX B: THERMOCOUPLE TYPE TEMPERATURE TOLERANCES
Tolerance contribution from measurement tolerances of +/-25µV, independent of tolerance contributions of cold junction compensation and individual TC sensors.
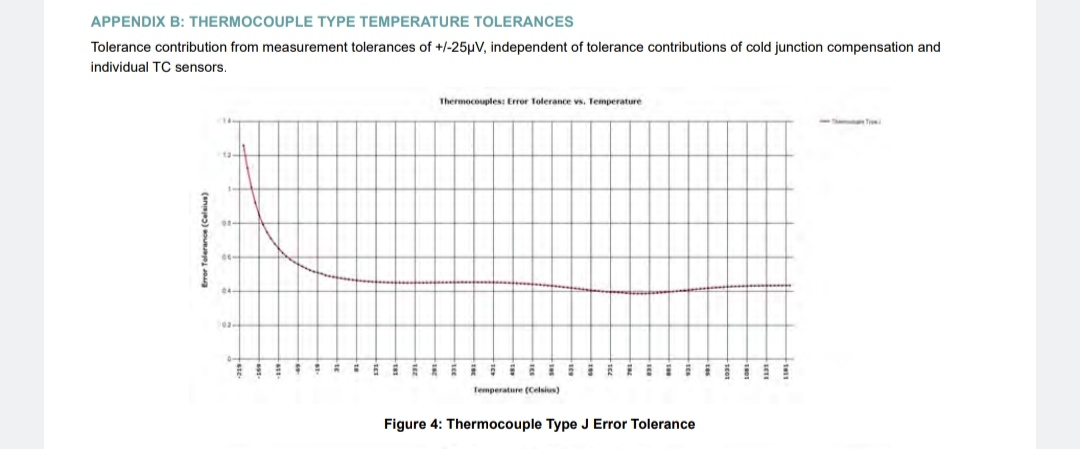
Figure 4. Thermocouple Type J Error Tolerance
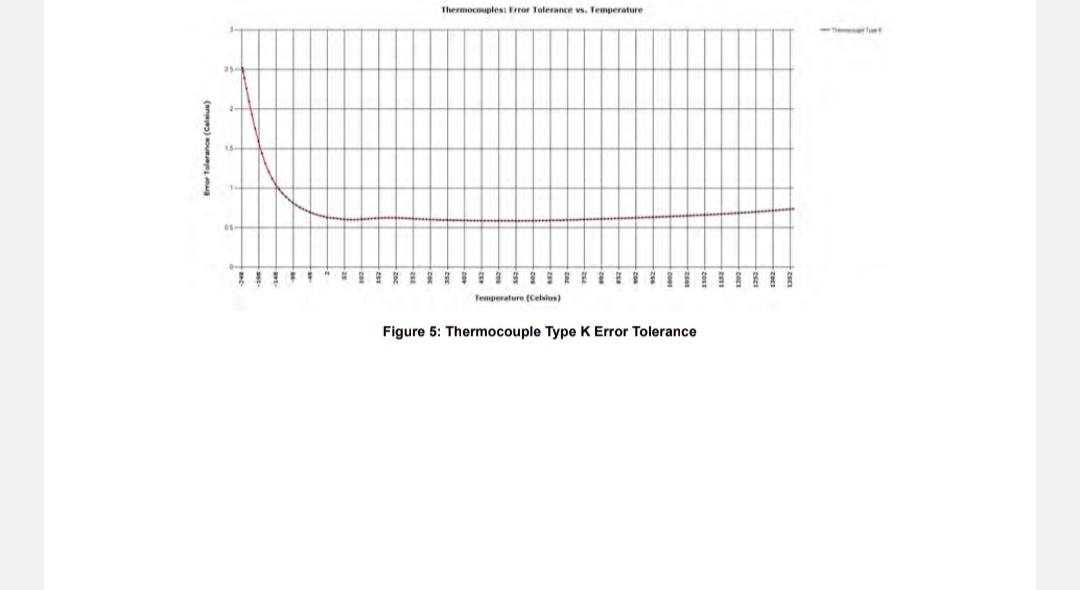
Figure 5. Thermocouple Type K Error Tolerance
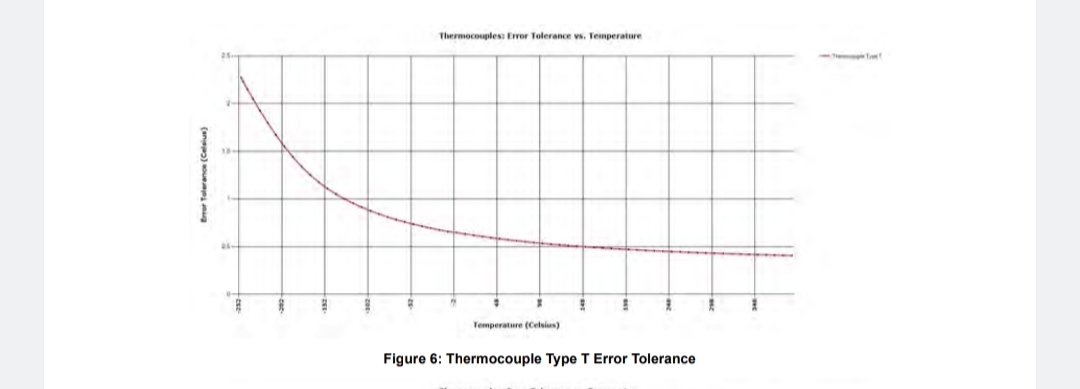
Figure 6. Thermocouple Type T Error Tolerance
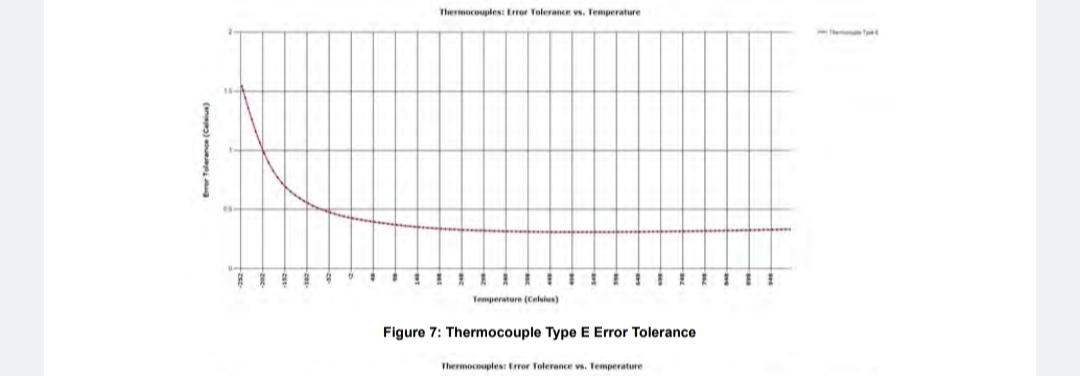
Figure 7. Thermocouple Type E Error Tolerance
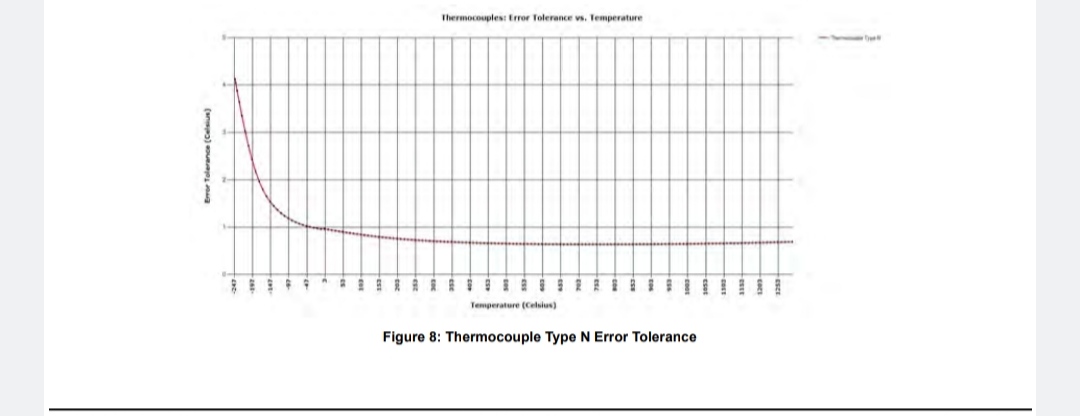
Figure 8. Thermocouple Type N Error Tolerance
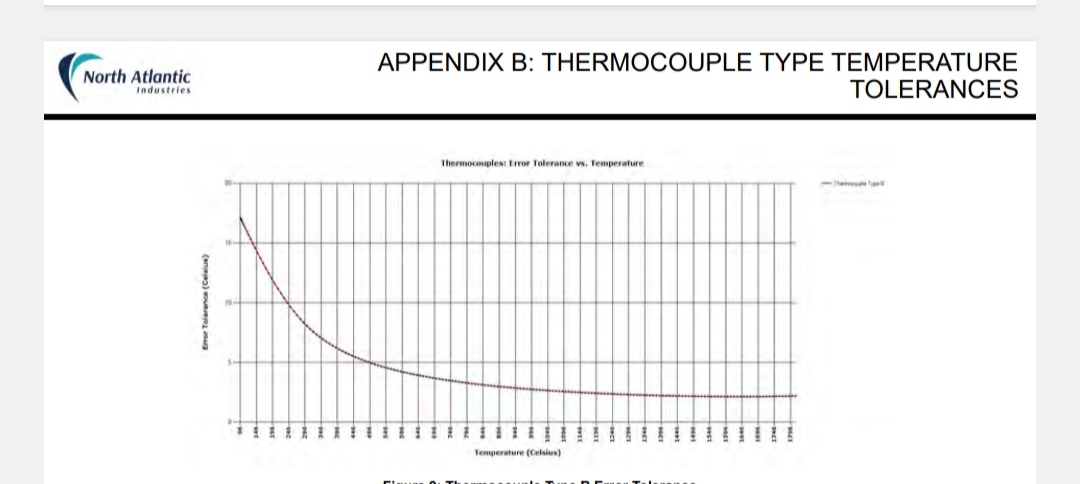
Figure 9. Thermocouple Type B Error Tolerance
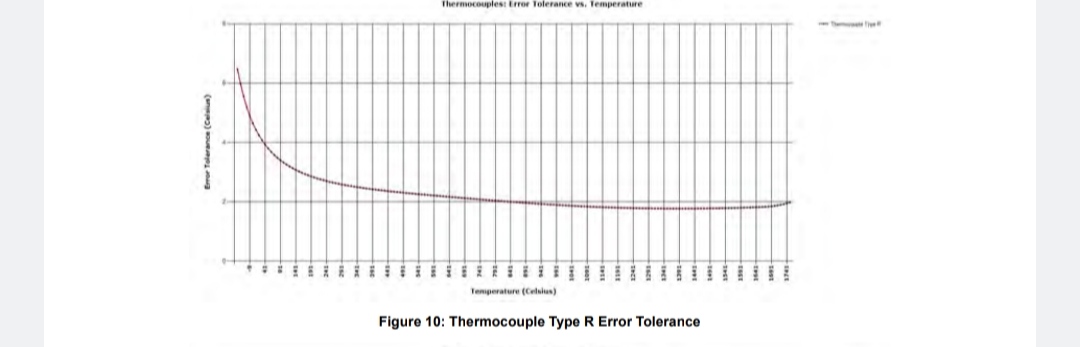
Figure 10. Thermocouple Type R Error Tolerance
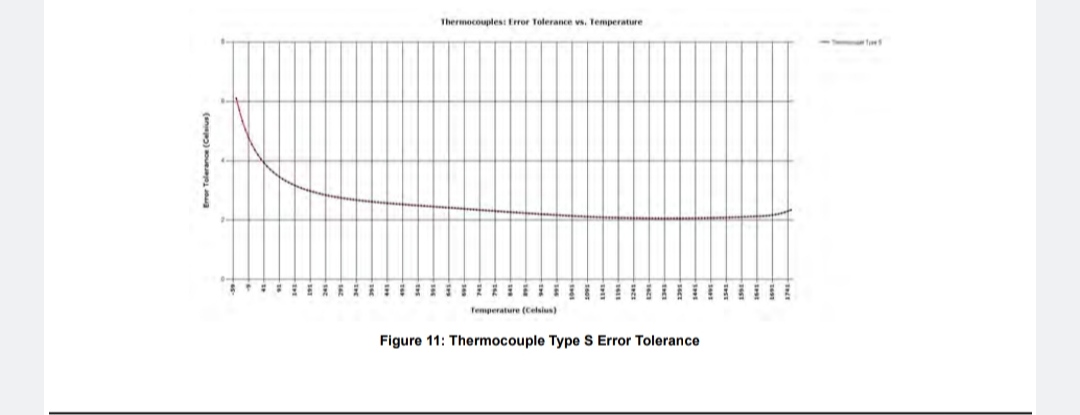
Figure 11. Thermocouple Type S Error Tolerance
APPENDIX C: PIN-OUT DETAILS
Pin-out details (for reference) are shown below, with respect to DATAIO. Additional information on pin-outs can be found in the Motherboard Operational Manuals.
Module Signal (Ref Only) |
44-Pin I/O |
50-Pin I/O (Mod Slot 1-J3) |
50-Pin I/O (Mod Slot 2-J4) |
50-Pin I/O (Mod Slot 3-J3) |
50-Pin I/O (Mod Slot 3-J4) |
RTD (RT1) |
Thermocouple (TC1) |
DATIO1 |
2 |
10 |
1 |
2 |
SENSE+_CH1 |
SENSE+_CH1 |
|
DATIO2 |
24 |
35 |
26 |
27 |
SENSE-_CH1 |
SENSE-_CH1 |
|
DATIO3 |
3 |
11 |
2 |
3 |
DRIVE+_CH1 |
||
DATIO4 |
25 |
36 |
27 |
28 |
DRIVE-_CH1 |
||
DATIO5 |
5 |
13 |
4 |
5 |
DRIVE+_CH2 |
||
DATIO6 |
27 |
38 |
29 |
30 |
DRIVE-_CH2 |
||
DATIO7 |
7 |
14 |
5 |
6 |
SENSE+_CH2 |
SENSE+_CH2 |
|
DATIO8 |
29 |
39 |
30 |
31 |
SENSE-_CH2 |
SENSE-_CH2 |
|
DATIO9 |
8 |
15 |
6 |
7 |
SENSE+_CH3 |
SENSE+_CH3 |
|
DATIO10 |
30 |
40 |
31 |
32 |
SENSE-_CH3 |
SENSE-_CH3 |
|
DATIO11 |
10 |
17 |
8 |
9 |
DRIVE+_CH3 |
||
DATIO12 |
32 |
42 |
33 |
34 |
DRIVE-_CH3 |
||
DATIO13 |
12 |
18 |
9 |
17 |
SENSE+_CH5 |
SENSE+_CH5 |
|
DATIO14 |
34 |
43 |
34 |
42 |
SENSE-_CH5 |
SENSE-_CH5 |
|
DATIO15 |
13 |
19 |
10 |
18 |
DRIVE+_CH5 |
||
DATIO16 |
35 |
44 |
35 |
43 |
DRIVE-_CH5 |
||
DATIO17 |
15 |
21 |
12 |
20 |
DRIVE+_CH6 |
||
DATIO18 |
37 |
46 |
37 |
45 |
DRIVE-_CH6 |
||
DATIO19 |
17 |
22 |
13 |
21 |
SENSE+_CH6 |
SENSE+_CH6 |
|
DATIO20 |
39 |
47 |
38 |
46 |
SENSE-_CH6 |
SENSE-_CH6 |
|
DATIO21 |
18 |
23 |
14 |
22 |
SENSE+_CH7 |
SENSE+_CH7 |
|
DATIO22 |
40 |
48 |
39 |
47 |
SENSE-_CH7 |
SENSE-_CH7 |
|
DATIO23 |
20 |
25 |
16 |
24 |
DRIVE+_CH7 |
||
DATIO24 |
42 |
50 |
41 |
49 |
DRIVE-_CH7 |
||
DATIO25 |
4 |
12 |
3 |
4 |
DRIVE+_CH4 |
||
DATIO26 |
26 |
37 |
28 |
29 |
DRIVE-_CH4 |
||
DATIO27 |
9 |
16 |
7 |
8 |
SENSE+_CH4 |
SENSE+_CH4 |
|
DATIO28 |
31 |
41 |
32 |
33 |
SENSE-_CH4 |
SENSE-_CH4 |
|
DATIO29 |
14 |
20 |
11 |
19 |
DRIVE+_CH8 |
DRIVE+_CH8 |
|
DATIO30 |
36 |
45 |
36 |
44 |
DRIVE-_CH8 |
DRIVE-_CH8 |
|
DATIO31 |
19 |
24 |
15 |
23 |
SENSE+_CH8 |
SENSE+_CH8 |
|
DATIO32 |
41 |
49 |
40 |
48 |
SENSE-_CH8 |
SENSE-_CH8 |
|
DATIO33 |
6 |
||||||
DATIO34 |
28 |
||||||
DATIO35 |
11 |
||||||
DATIO36 |
33 |
||||||
DATIO37 |
16 |
||||||
DATIO38 |
38 |
||||||
DATIO39 |
21 |
||||||
DATIO40 |
43 |
||||||
N/A |
FIRMWARE REVISION NOTES
This section identifies the firmware revision in which specific features were released. Prior revisions of the firmware would not support the features listed.
Feature |
Firmware Revision |
Release Date |
Channel Status Enabled |
1.6 |
|
Summary Status |
1.6 |
|
Suspend Maintenance Operations |
1.6 |
REVISION HISTORY
Motherboard Manual - TR1 Revision History |
||
Revision |
Revision Date |
Description |
C |
2022-09-29 |
ECO C09688, transition to docbuilder format. Replaced "Specifications" with "Data Sheet". Pg.6, added Pt2000 to RTD interface & excitation specs. Pg.6, changed Update Rate to Sample Rate; updated RTD spec. Pg.7, added Pt2000 to RTD Features. Pg.9, added Pt2000 range & excitation current source. Pg.10, added 3-wire mode excitation current description. Pg.12, changed Voltage op settings from micro-volts to volts. Pg.17, added Pt2000 to RTD Type. Pg.20, updated Channel Enable Status data range & initialized value. Pg.37, added Appendix C: Pin-Out Details. |
C1 |
2023-11-20 |
ECO C10979, pg.5, updated RTD Measurement feature bullets. Pg.6, corrected typo in Excitation spec. Pg.7-8, updated Introduction; added TR1 Overview. Pg.12/21/28, added module common registers. Pg.19, added note to 2-Wire Lead Resistance Compensation. Pg.23, removed summary events table. |
DOCS.NAII REVISIONS
Revision Date |
Description |
2025-03-13 |
Updated module pinout table to add module I/O pinouts for 44- & 50-pin connectors. |
STATUS AND INTERRUPTS
Edit this on GitLab
Status registers indicate the detection of faults or events. The status registers can be channel bit-mapped or event bit-mapped. An example of a channel bit-mapped register is the BIT status register, and an example of an event bit-mapped register is the FIFO status register.
For those status registers that allow interrupts to be generated upon the detection of the fault or the event, there are four registers associated with each status: Dynamic, Latched, Interrupt Enabled, and Set Edge/Level Interrupt.
Dynamic Status: The Dynamic Status register indicates the current condition of the fault or the event. If the fault or the event is momentary, the contents in this register will be clear when the fault or the event goes away. The Dynamic Status register can be polled, however, if the fault or the event is sporadic, it is possible for the indication of the fault or the event to be missed.
Latched Status: The Latched Status register indicates whether the fault or the event has occurred and keeps the state until it is cleared by the user. Reading the Latched Status register is a better alternative to polling the Dynamic Status register because the contents of this register will not clear until the user commands to clear the specific bit(s) associated with the fault or the event in the Latched Status register. Once the status register has been read, the act of writing a 1 back to the applicable status register to any specific bit (channel/event) location will “clear” the bit (set the bit to 0). When clearing the channel/event bits, it is strongly recommended to write back the same bit pattern as read from the Latched Status register. For example, if the channel bit-mapped Latched Status register contains the value 0x0000 0005, which indicates fault/event detection on channel 1 and 3, write the value 0x0000 0005 to the Latched Status register to clear the fault/event status for channel 1 and 3. Writing a “1” to other channels that are not set (example 0x0000 000F) may result in incorrectly “clearing” incoming faults/events for those channels (example, channel 2 and 4).
Interrupt Enable: If interrupts are preferred upon the detection of a fault or an event, enable the specific channel/event interrupt in the Interrupt Enable register. The bits in Interrupt Enable register map to the same bits in the Latched Status register. When a fault or event occurs, an interrupt will be fired. Subsequent interrupts will not trigger until the application acknowledges the fired interrupt by clearing the associated channel/event bit in the Latched Status register. If the interruptible condition is still persistent after clearing the bit, this may retrigger the interrupt depending on the Edge/Level setting.
Set Edge/Level Interrupt: When interrupts are enabled, the condition on retriggering the interrupt after the Latch Register is “cleared” can be specified as “edge” triggered or “level” triggered. Note, the Edge/Level Trigger also affects how the Latched Register value is adjusted after it is “cleared” (see below).
-
Edge triggered: An interrupt will be retriggered when the Latched Status register change from low (0) to high (1) state. Uses for edge-triggered interrupts would include transition detections (Low-to-High transitions, High-to-Low transitions) or fault detections. After “clearing” an interrupt, another interrupt will not occur until the next transition or the re-occurrence of the fault again.
-
Level triggered: An interrupt will be generated when the Latched Status register remains at the high (1) state. Level-triggered interrupts are used to indicate that something needs attention.
Interrupt Vector and Steering
When interrupts are enabled, the interrupt vector associated with the specific interrupt can be programmed with a unique number/identifier defined by the user such that it can be utilized in the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) to identify the type of interrupt. When an interrupt occurs, the contents of the Interrupt Vector registers is reported as part of the interrupt mechanism. In addition to specifying the interrupt vector, the interrupt can be directed (“steered”) to the native bus or to the application running on the onboard ARM processor.
Interrupt Trigger Types
In most applications, limiting the number of interrupts generated is preferred as interrupts are costly, thus choosing the correct Edge/Level interrupt trigger to use is important.
Example 1: Fault detection
This example illustrates interrupt considerations when detecting a fault like an “open” on a line. When an “open” is detected, the system will receive an interrupt. If the “open” on the line is persistent and the trigger is set to “edge”, upon “clearing” the interrupt, the system will not regenerate another interrupt. If, instead, the trigger is set to “level”, upon “clearing” the interrupt, the system will re-generate another interrupt. Thus, in this case, it will be better to set the trigger type to “edge”.
Example 2: Threshold detection
This example illustrates interrupt considerations when detecting an event like reaching or exceeding the “high watermark” threshold value. In a communication device, when the number of elements received in the FIFO reaches the high-watermark threshold, an interrupt will be generated. Normally, the application would read the count of the number of elements in the FIFO and read this number of elements from the FIFO. After reading the FIFO data, the application would “clear” the interrupt. If the trigger type is set to “edge”, another interrupt will be generated only if the number of elements in FIFO goes below the “high watermark” after the “clearing” the interrupt and then fills up to reach the “high watermark” threshold value. Since receiving communication data is inherently asynchronous, it is possible that data can continue to fill the FIFO as the application is pulling data off the FIFO. If, at the time the interrupt is “cleared”, the number of elements in the FIFO is at or above the “high watermark”, no interrupts will be generated. In this case, it will be better to set the trigger type to “level”, as the purpose here is to make sure that the FIFO is serviced when the number of elements exceeds the high watermark threshold value. Thus, upon “clearing” the interrupt, if the number of elements in the FIFO is at or above the “high watermark” threshold value, another interrupt will be generated indicating that the FIFO needs to be serviced.
Dynamic and Latched Status Registers Examples
The examples in this section illustrate the differences in behavior of the Dynamic Status and Latched Status registers as well as the differences in behavior of Edge/Level Trigger when the Latched Status register is cleared.
Figure 1. Example of Module’s Channel-Mapped Dynamic and Latched Status States
| No Clearing of Latched Status | Clearing of Latched Status (Edge-Triggered) | Clearing of Latched Status(Level-Triggered) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Time |
Dynamic Status |
Latched Status |
Action |
Latched Status |
Action |
Latched |
T0 |
0x0 |
0x0 |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
T1 |
0x1 |
0x1 |
Read Latched Register |
0x1 |
0x1 |
|
T1 |
0x1 |
0x1 |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
||
T1 |
0x1 |
0x1 |
0x0 |
0x1 |
||
T2 |
0x0 |
0x1 |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
Read Latched Register |
0x1 |
T2 |
0x0 |
0x1 |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
|
T2 |
0x0 |
0x1 |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
0x0 |
|
T3 |
0x2 |
0x3 |
Read Latched Register |
0x2 |
Read Latched Register |
0x2 |
T3 |
0x2 |
0x3 |
Write 0x2 to Latched Register |
Write 0x2 to Latched Register |
||
T3 |
0x2 |
0x3 |
0x0 |
0x2 |
||
T4 |
0x2 |
0x3 |
Read Latched Register |
0x1 |
Read Latched Register |
0x3 |
T4 |
0x2 |
0x3 |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
Write 0x3 to Latched Register |
||
T4 |
0x2 |
0x3 |
0x0 |
0x2 |
||
T5 |
0xC |
0xF |
Read Latched Register |
0xC |
Read Latched Register |
0xE |
T5 |
0xC |
0xF |
Write 0xC to Latched Register |
Write 0xE to Latched Register |
||
T5 |
0xC |
0xF |
0x0 |
0xC |
||
T6 |
0xC |
0xF |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
Read Latched |
0xC |
T6 |
0xC |
0xF |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
Write 0xC to Latched Register |
|
T6 |
0xC |
0xF |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
0xC |
|
T7 |
0x4 |
0xF |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
Read Latched Register |
0xC |
T7 |
0x4 |
0xF |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
Write 0xC to Latched Register |
|
T7 |
0x4 |
0xF |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
0x4 |
|
T8 |
0x4 |
0xF |
Read Latched Register |
0x0 |
Read Latched Register |
0x4 |
Interrupt Examples
The examples in this section illustrate the interrupt behavior with Edge/Level Trigger.
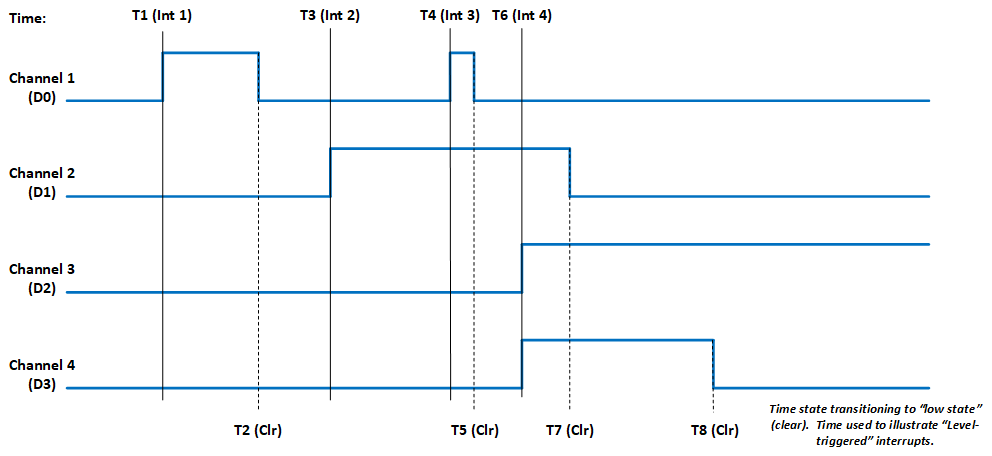
Figure 2. Illustration of Latched Status State for Module with 4-Channels with Interrupt Enabled
Time |
Latched Status (Edge-Triggered - Clear Multi-Channel) |
Latched Status (Edge-Triggered - Clear Single Channel) |
Latched Status (Level-Triggered - Clear Multi-Channel) |
|||
Action |
Latched |
Action |
Latched |
Action |
Latched |
|
T1 (Int 1) |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x1 |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x1 |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x1 |
T1 (Int 1) |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
|||
T1 (Int 1) |
0x0 |
0x0 |
Interrupt re-triggers Note, interrupt re-triggers after each clear until T2. |
0x1 |
||
T3 (Int 2) |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x2 |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x2 |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x2 |
T3 (Int 2) |
Write 0x2 to Latched Register |
Write 0x2 to Latched Register |
Write 0x2 to Latched Register |
|||
T3 (Int 2) |
0x0 |
0x0 |
Interrupt re-triggers Note, interrupt re-triggers after each clear until T7. |
0x2 |
||
T4 (Int 3) |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x1 |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x1 |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0x3 |
T4 (Int 3) |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
Write 0x1 to Latched Register |
Write 0x3 to Latched Register |
|||
T4 (Int 3) |
0x0 |
0x0 |
Interrupt re-triggers Note, interrupt re-triggers after each clear and 0x3 is reported in Latched Register until T5. |
0x3 |
||
T4 (Int 3) |
0x0 |
0x0 |
Interrupt re-triggers Note, interrupt re-triggers after each clear until T7. |
0x2 |
||
T6 (Int 4) |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0xC |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0xC |
Interrupt Generated Read Latched Registers |
0xE |
T6 (Int 4) |
Write 0xC to Latched Register |
Write 0x4 to Latched Register |
Write 0xE to Latched Register |
|||
T6 (Int 4) |
0x0 |
Interrupt re-triggers Write 0x8 to Latched Register |
0x8 |
Interrupt re-triggers Note, interrupt re-triggers after each clear and 0xE is reported in Latched Register until T7. |
0xE |
|
T6 (Int 4) |
0x0 |
0x0 |
Interrupt re-triggers Note, interrupt re-triggers after each clear and 0xC is reported in Latched Register until T8. |
0xC |
||
T6 (Int 4) |
0x0 |
0x0 |
Interrupt re-triggers Note, interrupt re-triggers after each clear and 0x4 is reported in Latched Register always. |
0x4 |
||
REVISION HISTORY
Motherboard Manual - Status and Interrupts Revision History |
||
Revision |
Revision Date |
Description |
C |
2021-11-30 |
C08896; Transition manual to docbuilder format - no technical info change. |
DOCS.NAII REVISIONS
Revision Date |
Description |
2026-03-02 |
Formatting updates to document; no technical changes. |
MODULE COMMON REGISTERS
Edit this on GitLab
The registers described in this document are common to all NAI Generation 5 modules.
Module Information Registers
The registers in this section provide module information such as firmware revisions, capabilities and unique serial number information.
FPGA Version Registers
The FPGA firmware version registers include registers that contain the Revision, Compile Timestamp, SerDes Revision, Template Revision and Zynq Block Revision information.
FPGA Revision |
|
Function: |
FPGA firmware revision |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the revision of the board’s FPGA |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are the major revision and the lower 16-bits are the minor revision. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Major Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
FPGA Compile Timestamp |
|
Function: |
Compile Timestamp for the FPGA firmware. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the compile timestamp of the board’s FPGA |
Operational Settings: |
The 32-bit value represents the Day, Month, Year, Hour, Minutes and Seconds as formatted in the table: |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
day (5-bits) |
month (4-bits) |
year (6-bits) |
hr |
||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
hour (5-bits) |
minutes (6-bits) |
seconds (6-bits) |
|||||||||||||
FPGA SerDes Revision |
|
Function: |
FPGA SerDes revision |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the SerDes revision of the board’s FPGA |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are the major revision, and the lower 16-bits are the minor revision. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Major Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
FPGA Template Revision |
|
Function: |
FPGA Template revision |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the template revision of the board’s FPGA |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are the major revision, and the lower 16-bits are the minor revision. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Major Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
FPGA Zynq Block Revision |
|
Function: |
FPGA Zynq Block revision |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the Zynq block revision of the board’s FPGA |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are the major revision, and the lower 16-bits are the minor revision. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Major Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
Bare Metal Version Registers
The Bare Metal firmware version registers include registers that contain the Revision and Compile Time information.
Bare Metal Revision |
|
Function: |
Bare Metal firmware revision |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the revision of the board’s Bare Metal |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are the major revision and the lower 16-bits are the minor revision. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Major Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
Bare Metal Compile Time |
|
Function: |
Provides an ASCII representation of the Date/Time for the Bare Metal compile time. |
Type: |
24-character ASCII string - Six (6) unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the ASCII representation of the compile time of the board’s Bare Metal |
Operational Settings: |
The six 32-bit words provide an ASCII representation of the Date/Time. The hexadecimal values in the field below represent: May 17 2019 at 15:38:32 |
|
Note
|
little-endian order of ASCII values |
Word 1 (Ex. 0x2079614D) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Space (0x20) |
Month ('y' - 0x79) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Month ('a' - 0x61) |
Month ('M' - 0x4D) |
||||||||||||||
Word 2 (Ex. 0x32203731) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Year ('2' - 0x32) |
Space (0x20) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Day ('7' - 0x37) |
Day ('1' - 0x31) |
||||||||||||||
Word 3 (Ex. 0x20393130) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Space (0x20) |
Year ('9' - 0x39) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Year ('1' - 0x31) |
Year ('0' - 0x30) |
||||||||||||||
Word 4 (Ex. 0x31207461) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Hour ('1' - 0x31) |
Space (0x20) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
'a' (0x74) |
't' (0x61) |
||||||||||||||
Word 5 (Ex. 0x38333A35) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Minute ('8' - 0x38) |
Minute ('3' - 0x33) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
':' (0x3A) |
Hour ('5' - 0x35) |
||||||||||||||
Word 6 (Ex. 0x0032333A) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
NULL (0x00) |
Seconds ('2' - 0x32) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Seconds ('3' - 0x33) |
':' (0x3A) |
||||||||||||||
FSBL Version Registers
The FSBL version registers include registers that contain the Revision and Compile Time information for the First Stage Boot Loader (FSBL).
FSBL Revision |
|
Function: |
FSBL firmware revision |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the revision of the board’s FSBL |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are the major revision, and the lower 16-bits are the minor revision. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Major Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
FSBL Compile Time |
|
Function: |
Provides an ASCII representation of the Date/Time for the FSBL compile time. |
Type: |
24-character ASCII string - Six (6) unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the ASCII representation of the Compile Time of the board’s FSBL |
Operational Settings: |
The six 32-bit words provide an ASCII representation of the Date/Time. |
The hexadecimal values in the field below represent: May 17 2019 at 15:38:32
|
Note
|
little-endian order of ASCII values |
Word 1 (Ex. 0x2079614D) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Space (0x20) |
Month ('y' - 0x79) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Month ('a' - 0x61) |
Month ('M' - 0x4D) |
||||||||||||||
Word 2 (Ex. 0x32203731) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Year ('2' - 0x32) |
Space (0x20) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Day ('7' - 0x37) |
Day ('1' - 0x31) |
||||||||||||||
Word 3 (Ex. 0x20393130) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Space (0x20) |
Year ('9' - 0x39) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Year ('1' - 0x31) |
Year ('0' - 0x30) |
||||||||||||||
Word 4 (Ex. 0x31207461) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Hour ('1' - 0x31) |
Space (0x20) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
'a' (0x74) |
't' (0x61) |
||||||||||||||
Word 5 (Ex. 0x38333A35) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Minute ('8' - 0x38) |
Minute ('3' - 0x33) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
':' (0x3A) |
Hour ('5' - 0x35) |
||||||||||||||
Word 6 (Ex. 0x0032333A) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
NULL (0x00) |
Seconds ('2' - 0x32) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Seconds ('3' - 0x33) |
':' (0x3A) |
||||||||||||||
Module Serial Number Registers
The Module Serial Number registers include registers that contain the Serial Numbers for the Interface Board and the Functional Board of the module.
Interface Board Serial Number |
|
Function: |
Unique 128-bit identifier used to identify the interface board. |
Type: |
16-character ASCII string - Four (4) unsigned binary words (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Serial number of the interface board |
Operational Settings: |
This register is for information purposes only. |
Functional Board Serial Number |
|
Function: |
Unique 128-bit identifier used to identify the functional board. |
Type: |
16-character ASCII string - Four (4) unsigned binary words (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
N/A |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Serial number of the functional board |
Operational Settings: |
This register is for information purposes only. |
Module Capability |
|
Function: |
Provides indication for whether or not the module can support the following: SerDes block reads, SerDes FIFO block reads, SerDes packing (combining two 16-bit values into one 32-bit value) and floating point representation. The purpose for block access and packing is to improve the performance of accessing larger amounts of data over the SerDes interface. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 0107 |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
0x0000 0107 |
Operational Settings: |
A “1” in the bit associated with the capability indicates that it is supported. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Flt-Pt |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Pack |
FIFO Blk |
Blk |
Module Memory Map Revision |
|
Function: |
Module Memory Map revision |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the Module Memory Map Revision |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are the major revision and the lower 16-bits are the minor revision. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Major Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor Revision Number |
|||||||||||||||
Module Measurement Registers
The registers in this section provide module temperature measurement information.
Temperature Readings Registers
The temperature registers provide the current, maximum (from power-up) and minimum (from power-up) Zynq and PCB temperatures.
Interface Board Current Temperature |
|
Function: |
Measured PCB and Zynq Core temperatures on Interface Board. |
Type: |
signed byte (8-bits) for PCB and signed byte (8-bits) for Zynq core temperatures |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the measured PCB and Zynq core temperatures based on the table below |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are not used, and the lower 16-bits are the PCB and Zynq Core Temperatures. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0000 202C, this represents PCB Temperature = 32° Celsius and Zynq Temperature = 44° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
PCB Temperature |
Zynq Core Temperature |
||||||||||||||
Functional Board Current Temperature |
|
Function: |
Measured PCB temperature on Functional Board. |
Type: |
signed byte (8-bits) for PCB |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the measured PCB on the table below |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 24-bits are not used, and the lower 8-bits are the PCB Temperature. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0000 0019, this represents PCB Temperature = 25° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
PCB Temperature |
|||||||
Interface Board Maximum Temperature |
|
Function: |
Maximum PCB and Zynq Core temperatures on Interface Board since power-on. |
Type: |
signed byte (8-bits) for PCB and signed byte (8-bits) for Zynq core temperatures |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the maximum measured PCB and Zynq core temperatures since power-on based on the table below |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are not used, and the lower 16-bits are the maximum PCB and Zynq Core Temperatures. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0000 5569, this represents maximum PCB Temperature = 85° Celsius and maximum Zynq Temperature = 105° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
PCB Temperature |
Zynq Core Temperature |
||||||||||||||
Interface Board Minimum Temperature |
|
Function: |
Minimum PCB and Zynq Core temperatures on Interface Board since power-on. |
Type: |
signed byte (8-bits) for PCB and signed byte (8-bits) for Zynq core temperatures |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the minimum measured PCB and Zynq core temperatures since power-on based on the table below |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits are not used, and the lower 16-bits are the minimum PCB and Zynq Core Temperatures. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0000 D8E7, this represents minimum PCB Temperature = -40° Celsius and minimum Zynq Temperature = -25° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
PCB Temperature |
Zynq Core Temperature |
||||||||||||||
Functional Board Maximum Temperature |
|
Function: |
Maximum PCB temperature on Functional Board since power-on. |
Type: |
signed byte (8-bits) for PCB |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the measured PCB on the table below |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 24-bits are not used, and the lower 8-bits are the PCB Temperature. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0000 0055, this represents PCB Temperature = 85° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
PCB Temperature |
|||||||
Functional Board Minimum Temperature |
|
Function: |
Minimum PCB temperature on Functional Board since power-on. |
Type: |
signed byte (8-bits) for PCB |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 00FF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Value corresponding to the measured PCB on the table below |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 24-bits are not used, and the lower 8-bits are the PCB Temperature. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0000 00D8, this represents PCB Temperature = -40° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
PCB Temperature |
|||||||
Higher Precision Temperature Readings Registers
These registers provide higher precision readings of the current Zynq and PCB temperatures.
Higher Precision Zynq Core Temperature |
|
Function: |
Higher precision measured Zynq Core temperature on Interface Board. |
Type: |
signed word (16-bits) for integer part and unsigned word (16-bits) for fractional part |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Measured Zynq Core temperature on Interface Board |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits represent the signed integer part of the temperature and the lower 16-bits represent the fractional part of the temperature with the resolution of 1/1000 of degree Celsius. For example, if the register contains the value 0x002B 0271, this represents Zynq Core Temperature = 43.625° Celsius, and value 0xFFF6 0177 represents -10.375° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Signed Integer Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Fractional Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
Higher Precision Interface PCB Temperature |
|
Function: |
Higher precision measured Interface PCB temperature. |
Type: |
signed word (16-bits) for integer part and unsigned word (16-bits) for fractional part |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Measured Interface PCB temperature |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits represent the signed integer part of the temperature and the lower 16-bits represent the fractional part of the temperature with the resolution of 1/1000 of degree Celsius. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0020 007D, this represents Interface PCB Temperature = 32.125° Celsius, and value 0xFFE8 036B represents -24.875° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Signed Integer Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Fractional Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
Higher Precision Functional PCB Temperature |
|
Function: |
Higher precision measured Functional PCB temperature. |
Type: |
signed word (16-bits) for integer part and unsigned word (16-bits) for fractional part |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
Measured Functional PCB temperature |
Operational Settings: |
The upper 16-bits represent the signed integer part of the temperature and the lower 16-bits represent the fractional part of the temperature with the resolution of 1/100 of degree Celsius. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0018 004B, this represents Functional PCB Temperature = 24.75° Celsius, and value 0xFFD9 0019 represents -39.25° Celsius. |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Signed Integer Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Fractional Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
Module Health Monitoring Registers
The registers in this section provide module temperature measurement information. If the temperature measurements reaches the Lower Critical or Upper Critical conditions, the module will automatically reset itself to prevent damage to the hardware.
Module Sensor Summary Status |
|
Function: |
The corresponding sensor bit is set if the sensor has crossed any of its thresholds. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bits) |
Data Range: |
See table below |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
This register provides a summary for module sensors. When the corresponding sensor bit is set, the Sensor Threshold Status register for that sensor will indicate the threshold condition that triggered the event. |
Bit(s) |
Sensor |
D31:D6 |
Reserved |
D5 |
Functional Board PCB Temperature |
D4 |
Interface Board PCB Temperature |
D3:D0 |
Reserved |
Module Sensor Registers
The registers listed in this section apply to each module sensor listed for the Module Sensor Summary Status register. Each individual sensor register provides a group of registers for monitoring module temperatures readings. From these registers, a user can read the current temperature of the sensor in addition to the minimum and maximum temperature readings since power-up. Upper and lower critical/warning temperature thresholds can be set and monitored from these registers. When a programmed temperature threshold is crossed, the Sensor Threshold Status register will set the corresponding bit for that threshold. The figure below shows the functionality of this group of registers when accessing the Interface Board PCB Temperature sensor as an example.
Sensor Threshold Status |
|
Function: |
Reflects which threshold has been crossed |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bits) |
Data Range: |
See table below |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
The associated bit is set when the sensor reading exceed the corresponding threshold settings. |
Bit(s) |
Description |
D31:D4 |
Reserved |
D3 |
Exceeded Upper Critical Threshold |
D2 |
Exceeded Upper Warning Threshold |
D1 |
Exceeded Lower Critical Threshold |
D0 |
Exceeded Lower Warning Threshold |
Sensor Current Reading |
|
Function: |
Reflects current reading of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents current sensor reading as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x41C6 0000 represents temperature = 24.75° Celsius. |
Sensor Minimum Reading |
|
Function: |
Reflects minimum value of temperature sensor since power up |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents minimum sensor value as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x41C6 0000 represents temperature = 24.75° Celsius. |
Sensor Maximum Reading |
|
Function: |
Reflects maximum value of temperature sensor since power up |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents maximum sensor value as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x41C6 0000 represents temperature = 24.75° Celsius. |
Sensor Lower Warning Threshold |
|
Function: |
Reflects lower warning threshold of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
Default lower warning threshold (value dependent on specific sensor) |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents sensor lower warning threshold as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0xC220 0000 represents temperature = -40.0° Celsius. |
Sensor Lower Critical Threshold |
|
Function: |
Reflects lower critical threshold of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
Default lower critical threshold (value dependent on specific sensor) |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents sensor lower critical threshold as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0xC25C 0000 represents temperature = -55.0° Celsius. |
Sensor Upper Warning Threshold |
|
Function: |
Reflects upper warning threshold of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
Default upper warning threshold (value dependent on specific sensor) |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents sensor upper warning threshold as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x42AA 0000 represents temperature = 85.0° Celsius. |
Sensor Upper Critical Threshold |
|
Function: |
Reflects upper critical threshold of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
Default upper critical threshold (value dependent on specific sensor) |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents sensor upper critical threshold as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x42FA 0000 represents temperature = 125.0° Celsius. |
FUNCTION REGISTER MAP
KEY
Configuration/Control |
Measurement/Status/Board Information |
| MODULE INFORMATION REGISTERS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
OFFSET |
REGISTER NAME |
ACCESS |
OFFSET |
REGISTER NAME |
ACCESS |
0x003C |
FPGA Revision |
R |
0x0074 |
Bare Metal Revision |
R |
0x0030 |
FPGA Compile Timestamp |
R |
0x0080 |
Bare Metal Compile Time (Bit 0-31) |
R |
0x0034 |
FPGA SerDes Revision |
R |
0x0084 |
Bare Metal Compile Time (Bit 32-63) |
R |
0x0038 |
FPGA Template Revision |
R |
0x0088 |
Bare Metal Compile Time (Bit 64-95) |
R |
0x0040 |
FPGA Zynq Block Revision |
R |
0x008C |
Bare Metal Compile Time (Bit 96-127) |
R |
0x0090 |
Bare Metal Compile Time (Bit 128-159) |
R |
|||
0x0094 |
Bare Metal Compile Time (Bit 160-191) |
R |
|||
0x007C |
FSBL Revision |
R |
|||
0x00B0 |
FSBL Compile Time (Bit 0-31) |
R |
|||
0x00B4 |
FSBL Compile Time (Bit 32-63) |
R |
|||
0x00B8 |
FSBL Compile Time (Bit 64-95) |
R |
|||
0x00BC |
FSBL Compile Time (Bit 96-127) |
R |
|||
0x00C0 |
FSBL Compile Time (Bit 128-159) |
R |
|||
0x00C4 |
FSBL Compile Time (Bit 160-191) |
R |
|||
0x0000 |
Interface Board Serial Number (Bit 0-31) |
R |
0x0010 |
Functional Board Serial Number (Bit 0-31) |
R |
0x0034 |
Interface Board Serial Number (Bit 32-63) |
R |
0x0014 |
Functional Board Serial Number (Bit 32-63) |
R |
0x0008 |
Interface Board Serial Number (Bit 64-95) |
R |
0x0018 |
Functional Board Serial Number (Bit 64-95) |
R |
0x000C |
Interface Board Serial Number (Bit 96-127) |
R |
0x001C |
Functional Board Serial Number (Bit 96-127) |
R |
0x0070 |
Module Capability |
R |
|||
0x01FC |
Module Memory Map Revision |
R |
|||
MODULE MEASUREMENTS REGISTERS |
|||||
OFFSET |
REGISTER NAME |
ACCESS |
OFFSET |
REGISTER NAME |
ACCESS |
0x0200 |
Interface Board PCB/Zynq Current Temp |
R |
0x0208 |
Functional Board PCB Current Temp |
R |
0x0218 |
Interface Board PCB/Zynq Max Temp |
R |
0x0228 |
Functional Board PCB Max Temp |
R |
0x0220 |
Interface Board PCB/Zynq Min Temp |
R |
0x0230 |
Functional Board PCB Min Temp |
R |
0x02C0 |
Higher Precision Zynq Core Temperature |
R |
|||
0x02C4 |
Higher Precision Interface PCB Temperature |
R |
|||
0x02E0 |
Higher Precision Functional PCB Temperature |
R |
|||
MODULE HEALTH MONITORING REGISTERS |
|||||
OFFSET |
REGISTER NAME |
ACCESS |
OFFSET |
REGISTER NAME |
ACCESS |
0x07F8 |
Module Sensor Summary Status |
R |
|||
|
|||||
REVISION HISTORY
Motherboard Manual - Module Common Registers Revision History |
||
Revision |
Revision Date |
Description |
C |
2023-08-11 |
ECO C10649, initial release of module common registers manual. |
C1 |
2024-05-15 |
ECO C11522, removed Zynq Core/Aux/DDR Voltage register descriptions from Module Measurement Registers. Pg.16, updated Module Sensor Summary Status register to add PS references; updated Bit Table to change voltage/current bits to 'reserved'. Pg.16, updated Module/Power Supply Sensor Registers description to better describe register functionality and to add figure. Pg.17, added 'Exceeded' to threshold bit descriptions. Pg.17-18, removed voltage/current references from sensor descriptions. Pg.20, removed Zynq Core/Aux/DDR Voltage register offsets from Module Measurement Registers. Pg.20, updated Module Health Monitoring Registers offset tables. |
C2 |
2024-07-10 |
ECO C11701, pg.16, updated Module Sensor Summary Status register to remove PS references;updated Bit Table to change PS temperature bits to 'reserved'. Pg.16, updated Module SensorRegisters description to remove PS references. Pg.20, updated Module Health MonitoringRegisters offset tables to remove PS temperature register offsets. |
DOCS.NAII REVISIONS
Revision Date |
Description |
2025-11-05 |
Corrected register offsets for Interface Board Min Temp and Function Board Min & Max Temps. |
2026-03-02 |
Formatting updates to document; no technical changes. |
NAI Cares
Edit this on GitLab
North Atlantic Industries (NAI) is a leading independent supplier of Embedded I/O Boards, Single Board Computers, Rugged Power Supplies, Embedded Systems and Motion Simulation and Measurement Instruments for the Military, Aerospace and Industrial Industries. We accelerate our clients’ time-to-mission with a unique approach based on a Configurable Open Systems Architecture™ (COSA®) that delivers the best of both worlds: custom solutions from standard COTS components.
We have built a reputation by listening to our customers, understanding their needs, and designing, testing and delivering board and system-level products for their most demanding air, land and sea requirements. If you have any applications or questions regarding the use of our products, please contact us for an expedient solution.
Please visit us at: www.naii.com or select one of the following for immediate assistance: