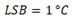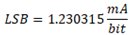68PW1 Manual
Edit this on GitLab
INTRODUCTION
NAI is a leading manufacturer of products that support advanced control systems, including PWM servo motor drives. These drives primarily provide precise power/current drive utilizing pulse-width modulation (PWM) technology. Servo motors are commonly used in industrial automation, turret and imaging control, robotics, and other precision motion control systems. NAI’s PWM servo motor drives are designed for higher-power and with external or built-in closed-loop feedback options, can achieve speed and position control of servo motors for performance motion control applications.
68PW1 Overview
The 68PW1 is a single-axis PWM servo motor drive. The 68PW1 offers high-performance motion control for a variety of industrial applications and is designed for use in rugged environments. This 3U OpenVPX module is conduction-cooled and supports VPX profiles:
-
MOD3-PAY-2U2U-16.2.16-1
-
SLT3-PAY-2U2U-14.2.17
The 68PW1 PWM drive supports both 2-phase brushed and 3-phase brushless (BLDC) motor types. A 2-phase brushed motor is a type of DC motor that uses a commutator and brushes to supply current to the rotor. It has a simple construction and is known for its low cost, high starting torque, and ease of control. However, wear and tear to the brushes can limit its lifespan. A 3-phase brushless (BLDC) motor uses a permanent magnet rotor and an electronic commutation system to provide more precise control and longer lifespan. It is more efficient, dependable, and produces less noise and vibration than a brushed motor. However, its construction is more complex and expensive. BLDC motors are commonly used in high-performance applications such as aerospace, automotive, and robotics.
From a single +28 VDC input source, the 68PW1 provides a programmable PWM output drive that can range from 24 V to 65 V. The card can source up to 10 A of current, providing a maximum power output of 650 W. The drive also includes discrete drive-enable control pins and P2/P3 TE high-current blade connectors, ensuring reliable and secure motor control.
The 68PW1 features a range of ancillary I/O options, including:
-
Four (4) ±10V A/D channels, with the first channel input set by default for injection into the current command for debugging & analysis purposes.
-
Four (4) ±10V D/A channels, which by default are configured as Channels 1 and 2 Feedback Current & Channels 1 and 2 Current Command outputs for testing & analysis purposes.
-
One (1) RS-422/485 SDLC serial communication channel, which provides a high-speed communication interface for a range of control and monitoring applications. For example, it can connect the drive to a remote controller or PLC, allowing for remote monitoring and control of the motor.
-
One (1) RS-232 console/debug channel, which can be used for console or debug purposes, allowing for easy setup, and troubleshooting of the drive. It can also interface with a local computer or other control device, allowing for direct control and monitoring of the motor.
-
One (1) 10/100BASE-T port, which provides a high-speed network connection for remote control and monitoring of the motor, as well as for maintenance and diagnostics. For example, it can remotely monitor and adjust the motor’s performance, or provide real-time status updates to a control system.
-
One (1) GbE (1000BASE-KX) port, which allows for remote control and monitoring of the motor drive system through an Ethernet connection. For instance, a computer or other control device can access and control the motor drive over a local network, which can be useful in situations where the motor drive is in a hard-to-reach location or needs remote monitoring for maintenance purposes. Additionally, this option allows for integration of the motor drive with other networked devices in a larger system for centralized control and monitoring.
The 68PW1 motor drive also supports the following feedback and control options:
-
Hall, needed for BLDC motor commutation.
-
Resolver/Synchro + AC Reference, commonly used in applications where the motor is subjected to harsh environments and high shock or vibration conditions, such as in military, aerospace, or oil drilling systems. This variety of feedback provides accurate positioning data with excellent resistance to electrical interference.
-
Encoder, widely used in industrial automation and robotics applications that require precise control of the position and speed of a motor. One example is in CNC machines where accurate control of the cutting tool is necessary to achieve high precision machining of parts.
The 68PW1 includes IPMC support for VITA 46.11 Tier-2, basic, compatible (configured option). The card is powered using +12V, ±12V AUX, and +3.3V AUX inputs, with a typical power dissipation of 10 W and an estimated 96% efficiency for the PWM drive.
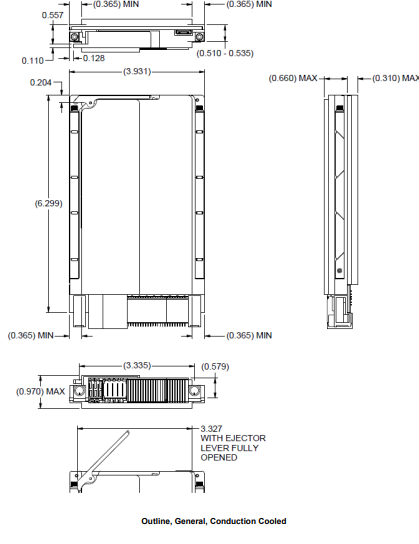
The modular and programmable architecture of the 68PW1 allows for flexible integration with a variety of systems and is supported by an intelligent I/O library. It is suitable for use in both commercial and rugged applications, with an operating temperature range of -40º C to 85º C. In addition, the drive’s mechanical envelope is ANSI/VITA 48 compatible with a 1.0” pitch, and has a weight of approximately 1.95 lbs.
SOFTWARE SUPPORT
The ENAIBL Software Support Kit (SSK) is supplied with all system platform-based board level products. This platform’s SSK contents include html format help documentation which defines board specific library functions and their respective parameter requirements. A board specific library and its source code is provided (module level ‘C' and header files) to facilitate function implementation independent of user operating system (O/S). Portability files are provided to identify Board Support Package (BSP) dependent functions and help port code to other common system BSPs. With the use of the provided help documentation, these libraries are easily ported to any 32-bit O/S such as RTOS or Linux.
The latest version of a board specific SSK can be downloaded from our website www.naii.com in the software downloads section. A Quick-Start Software Manual is also available for download where the SSK contents are detailed, Quick-Start Instructions provided, and GUI applications are described therein. For other operating system support, contact factory.
SPECIFICATIONS
General for the Motherboard
Signal Logic Level: |
Supports LVDS PCIe ver. 2.0 bus (x1) |
Power (Motherboard): |
+12V @ 900 mA (at no load conditions) +12V_AUX @ 45 mA -12V_AUX @ 45 mA +3.3V_AUX @ 350 mA |
Temperature, Operating: |
"C" =0° C to +70° C, "H" =-40° C to +85° C (see part number) |
Storage Temperature: |
-55° C to +105° C |
Temperature Cycling: |
Each board is cycled from -40° C to +85° C for options “C” or “H” |
General size: |
Height: 3.94" / 100 mm (3U) Width: 0.8" / 20.3 mm (4HP) or 1.0” / 25.4 mm (5 HP) air cooled front panel options Depth: 6.3“ / 160 mm deep |
Weight: |
1.95 lbs. (0.88 kg) (approx.) (conduction cooled) |
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
REGISTER MEMORY MAP ADDRESSING
The register map address consists of the following:
-
cPCI/PCIe BAR or Base Address for the Board
-
PWM Base Address
-
Function Offset Address
Board Base Address
The table below lists the BAR used for access to the motherboard and PWM registers. The second BAR is used internally for motherboard and PWM firmware updates. The other cPCI/PCIe BARs not listed are not used.
NAI Boards |
Device ID |
Bus |
Motherboard and Module Register Access |
Motherboard and Module Firmware Updates |
Slave Boards |
||||
68PW1 |
0x6888 |
PCIe |
BAR 1 Size: Module Dependent (minimum 64K Bytes) |
BAR 2 Size: 1M Bytes |
PWM Slot and Function Addresses
The 68PW1 includes a preconfigured PWM drive embedded within the motherboard (onboard function). This onboard function is the equivalent of a standard NAI COSA smart function module. The “start” address of the onboard PWM function register area is factory pre-defined (and read from) the motherboard PWM Start Address register. Refer to page 65 for the complete PWM Function Register Map.
Address Calculation
Motherboard Registers:
Read/Write access to the motherboard registers starts with the base address for the board and then the motherboard base offset address. For example, to address the onboard PWM Start Address register (i.e. register address = 0x0400):
-
Start with the base address for the board.
-
Add the motherboard base register address offset.
Motherboard Address = |
Base Address + Motherboard Address Offset |
= 0x0000 0400 |
0x0000 0000 + 0x0400 |
PWM Registers:
Read/Write access to the onboard PWM’s registers start with the base address of the board. Add the “content” for the PWM Start Address and then, add the specific onboard PWM function register offset.
For example, to address an appropriate/specific PWM with a register offset:
-
Start with the base address for the board.
-
Add the value (contents) from the onboard PWM base address offset register (contents/value of Motherboard Memory register for the onboard PWM (i.e., @ 0x0400) = 0x4000.
-
Then add the specific PWM function Register Offset of interest (i.e., ADC Test Input Ch 1 @ 0x0200)
(PWM Function Specific) Address = |
Base Address |
PWM Base Address Offset |
Function Register Offset |
= 0x0000 4200 |
0x0000 0000 |
0x4000 |
0x0200 |
MOTHERBOARD REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
PWM Information Registers
The PWM Addressing Ready, PWM Address, PWM Size and PWM ID provide information about the onboard PWM detected on the board. PWM Addressing Ready
PWM Addressing Ready
Function: Indicates that the onboard PWM is ready to be addressed.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0xA5A5A5A5
Operational Settings: This register will contain the value of 0xA5A5A5A5 when the PWM address has been determined.
PWM Address
Function: Specifies the Base Address for the onboard PWM.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: Based on board’s PWM configuration.
PWM Size
Function: Specifies the Memory Size (in bytes) allocated for the onboard PWM.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: Assigned by factory for the PWM.
PWM ID
Function: Specifies the PWM ID for the onboard PWM.
Type: 4-character ASCII string
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: Assigned by factory for the PWM.
Operational Settings: The PWM ID is formatted as four ASCII bytes: three characters followed by a space. The PWM ID is in little-endian order with a single space following the first three characters.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
ASCII Character (ex: 'P' - 0x50) |
ASCII Character (ex: 'W' - 0x57) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
ASCII Character (ex: '1' - 0x31) |
ASCII Space (' ' - 0x20) |
||||||||||||||
Hardware Information Registers
The registers identified in this section provide information about the board’s hardware.
Product Serial Number
Function: Specifies the Board Serial Number.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: Serial number assigned by factory for the board.
Operational Settings: N/A
Platform
Function: Specifies the Board Platform Identifier. Values are for the ASCII characters for the NAI valid platforms (Identifiers).
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: See table below.
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: ASCII code is for the Platform Identifier of the board.
Operational Settings: Valid NAI platforms and the associated values for these platforms are shown below:
NAI Platform |
Platform Identifier |
ASCII Binary Values (Note: little-endian order of ascii values) |
3U VPX |
68 |
0x0000 3836 |
Model
Function: Specifies the Board Model Identifier. Values are for the ASCII characters for the NAI valid models.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: See table below.
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: ASCII code is for the Model Identifier of the board.
Operational Settings: Examples of NAI models and the associated values for these models are shown below:
NAI Model |
ASCII Binary Values (Note: little-endian order of ascii values) |
PW |
0x0000 5057 |
Generation
Function: Specifies the Board Generation. Identifier values are for the ASCII characters for the NAI valid generation identifiers.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: See table below.
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: ASCII code is for the Generation Identifier of the board.
Operational Settings: Examples of NAI generations and the associated values for these generations are shown below:
NAI Generation |
ASCII Binary Values (Note: little-endian order of ascii values) |
1 |
0x0000 0031 |
Processor Count/Ethernet Count
Function: Specifies the Processor Count and Ethernet Count
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: See table below.
Read/Write: R
Operational Settings:
Processor Count - Indicates the number of unique processor types on the motherboard.
NAI Board |
Processor Count |
Description |
|
3U-VPX |
68PW1 |
1 |
Xilinx Zynq 7015 |
Ethernet Interface Count - Indicates the number of Ethernet interfaces on the product motherboard. For example, Single Ethernet = 1; Dual Ethernet = 2.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Processor Count (See Table) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Ethernet Count (Based on Part Number Ethernet Options) |
|||||||||||||||
Maximum Module Slot Count/ARM Platform Type
Function: Specifies the Maximum Module Slot Count and ARM Platform Type.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: See table below.
Read/Write: R
Operational Settings:
Maximum Module Slot Count - Indicates the number of modules that can be installed on the product.
ARM Platform - Altera = 1; Xilinx X1 = 2; Xilinx X2 = 3; UltraScale = 4
|
Note
|
The onboard PWM function is the equivalent of one (1) smart function module. |
NAI Board |
Maximum Module Slot Count |
ARM Platform Type |
|
3U-VPX |
68PW1 |
1 |
Xilinx X2 = 3 |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Maximum Module Slot Count (See Table) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
ARM Platform Type (See Table) |
|||||||||||||||
Motherboard Firmware Information Registers
The registers in this section provide information on the revision of the firmware installed on the motherboard.
Motherboard Core (MBCore) Firmware Version
Function: Specifies the Version of the NAI factory provided Motherboard Core Application installed on the board.
Type: Two (2) unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Operational Settings: The motherboard firmware version consists of four components: Major, Minor, Minor 2, and Minor 3.
Word 1 (Ex. 0007 0004 = 4.7 (Major.Minor) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Minor (ex: 0x0007 = 7) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Major (ex: 0x0004 = 4) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 2 (Ex. 0x0000 0000 = 0000 = 0.0 (Minor2.Minor3)) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Minor 3 (ex: 0x000 = 0) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor 2 (ex: 0x000 = 0) |
|||||||||||||||
Motherboard Firmware Build Date/Time
Function: Specifies the Build Date/Time of the NAI factory provided Motherboard Core Application installed on the board.
Type: Two (2) unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: N/A
Read/Write: R
Operational Settings: The motherboard firmware time consists of the Build Date and Build Time.
|
Note
|
On some builds the Date/Time fields are fixed to 0000 0000 to maintain binary consistency across builds. |
Word 1 - Build Date (ex. 0x030C 07E2 = 2018-12-03) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Day (ex: 0x03 = 3) |
Month (ex: 0x0C = 12) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Year (ex: 0x07E2 = 2018) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 2 – Build Time (ex. 0x001B 3B0A = 10:59:27) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
null (0x00) |
Seconds (ex: 0x1B = 27) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minutes (ex: 0x3B = 59) |
Hours (ex: 0x0A = 10) |
||||||||||||||
Motherboard FPGA Revision
Function: Specifies the revision of the NAI factory provided Motherboard FPGA installed on the board.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Operational Settings: The motherboard FPGA revision consists of two components: Major, Minor.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Major (ex: 0x0005 = 5) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Minor (ex: 0x0008 = 8) |
|||||||||||||||
Motherboard FPGA Compile Date/Time
Function: Specifies the Compile Date/Time of the NAI factory provided Motherboard FPGA installed on the board.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: N/A
Read/Write: R
Operational Settings: The motherboard FPGA time consists of the Build Date and Time in the following format:
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Day (D31:D27) |
Month (D26:D23) |
Year (D22:D17) |
|||||||||||||
ex. 0xD |
ex. 0x1 |
0x2 |
0xA |
||||||||||||
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
Day = 0x1A = 26 |
Month = 0x2 = 2 |
Year = 0x15 = 21 |
|||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Hour (D16:D12) |
Minutes (D11:D6) |
Seconds (D5:D0) |
|||||||||||||
ex. 0x0 |
ex. 0x1 |
ex. 0xB |
ex. 0x8 |
||||||||||||
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Hour = 0x00 = 0 |
Minutes = 0x06 |
Seconds = 0x38 = 56 |
|||||||||||||
Motherboard Monitoring Registers
The registers in this provide motherboard temperature measurement information, and where applicable the host processor and slave processor measurements.
NAI Boards |
Bus |
Has Host Processor |
Has Slave Processor |
Slave Boards |
68PW1 |
PCIe |
No |
Temperature Readings Register
The temperature registers provide the current, maximum (from power-up) and minimum (from power-up) for the processor and PCB for Zynq processor.
These registers are only available on Xilinx Generation 5 platforms, and are periodically populated by the motherboard core application, which only runs in Petalinux and BareMetal. For other operating systems, refer to the naibrd Software Support Kit (SSK) naibsp_system_Monitor_Temperature_Get() routine to manually retrieve the temperature (NOTE: this feature is typically utilized for development/factory use only; contact the factory for additional details on potential use, if required).
Function: Specifies the Measured Temperatures on Motherboard.
Type: signed byte (8-bits) for each temperature reading – Six (6) 32-bit words
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0x0000 FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: Value corresponding to the measured temperatures based on the table below.
Operational Settings: The 8-bit temperature readings are signed bytes. For example, if the following register contains the value 0x6955 0000: Example:
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Max Zynq Core Temperature |
Max Zynq PCB Temperature |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0x00 |
0x00 |
||||||||||||||
The values would represent the following temperatures:
Temperature Measurements |
Data Bits |
Value |
Temperature (Celsius) |
Max Zynq Core Temperature |
D31:D24 |
0x69 |
+105° |
Max Zynq PCB Temperature |
D23:D16 |
0x55 |
+85° |
Word 1 (Current Zynq Temperatures) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Zynq Core Temperature |
Zynq PCB Temperature |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0x00 |
0x00 |
||||||||||||||
Word 2 (Reserved) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0x00 |
0x00 |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0x00 |
0x00 |
||||||||||||||
Word 3 (Max Zynq Temperatures) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Zynq Core Max |
Temp Zynq PCB Max Temp |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0x00 |
0x00 |
||||||||||||||
Word 4 (Reserved) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0x00 |
0x00 |
||||||||||||||
Word 5 (Min Zynq Temperatures) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Min Zynq Core Temperature |
Min Zynq PCB Temperature |
||||||||||||||
Word 6 (Reserved) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0x00 |
0x00 |
||||||||||||||
Higher Precision Temperature Readings Register
These registers provide higher precision readings of the current Zynq and PCB temperatures.
Higher Precision Zynq Core Temperature
Function: Specifies the Higher Precision Measured Zynq Core temperature on Interface Board.
Type: signed word (16-bits) for integer part and unsigned word (16-bits) for fractional part
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: Measured Zynq Core temperature on Interface Board.
Operational Settings: The upper 16-bits represent the signed integer part of the temperature, and the lower 16-bits represent the fractional part of the temperature with the resolution of 1/1000 of degree Celsius. For example, if the register contains the value 0x002B 0271, this represents Zynq Core Temperature = 43.625° Celsius, and value 0xFFF6 0177 represents -10.375° Celsius.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Signed Integer Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Fractional Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
Higher Precision Motherboard PCB Temperature
Function: Specifies the Higher Precision Measured Motherboard PCB temperature.
Type: signed word (16-bits) for integer part and unsigned word (16-bits) for fractional part
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: Measured Motherboard PCB temperature.
Operational Settings: The upper 16-bits represent the signed integer part of the temperature, and the lower 16-bits represent the fractional part of the temperature with the resolution of 1/1000 of degree Celsius. For example, if the register contains the value 0x0020 007D, this represents Interface PCB Temperature = 32.125° Celsius, and value 0xFFE8 036B represents -24.875° Celsius.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Signed Integer Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Fractional Part of Temperature |
|||||||||||||||
Motherboard Health Monitoring Registers
The registers in this section provide a summary of motherboard temperature sensors and their corresponding bits. Additionally, this section provides an overview of the registers allocated to those sensors, which are used to monitor current/minimum/maximum temperature readings, upper & lower critical/warning temperature thresholds, and whether or not a programmed temperature threshold has been exceeded.
These registers are only available on Xilinx Generation 5 platforms, and are periodically populated by the motherboard core application, which only runs in Petalinux and BareMetal. For other operating systems, refer to the naibrd Software Support Kit (SSK) naibsp_system_Monitor_Temperature_Get() routine to manually retrieve the temperature (NOTE: this feature is typically utilized for development/factory use only; contact the factory for additional details on potential use, if required).
Motherboard Sensor Summary Status
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
The corresponding sensor bit is set if the sensor has crossed any of its thresholds. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bits) |
Data Range: |
See table below |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
This register provides a summary for motherboard sensors. When the corresponding sensor bit is set, the Sensor Threshold Status register for that sensor will indicate the threshold condition that triggered the event. |
Bit(s) |
Sensor |
D31:D5 |
Reserved |
D4 |
Motherboard PCB Temperature |
D3 |
Zynq Core Temperature |
D2:D0 |
Reserved |
Motherboard Sensor Registers
Edit this on GitLab
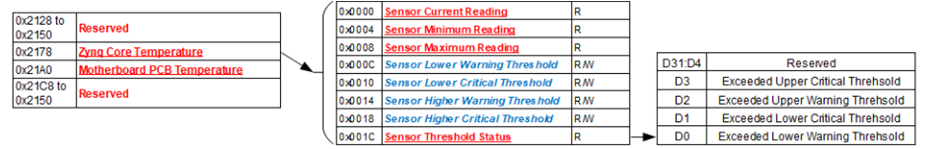
The registers listed in this section apply to each module sensor listed for the Motherboard Sensor Summary Status register. Each individual sensor register provides a group of registers for monitoring motherboard temperatures readings. From these registers, a user can read the current temperature of the sensor in addition to the minimum and maximum temperature readings since power-up. Upper and lower critical/warning temperature thresholds can be set and monitored from these registers. When a programmed temperature threshold is crossed, the Sensor Threshold Status register will set the corresponding bit for that threshold. The figure below shows the functionality of this group of registers when accessing the Zynq Core Temperature sensor as an example.
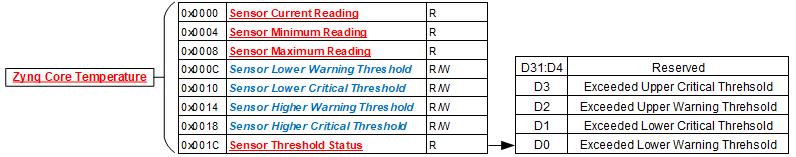
Sensor Threshold Status
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Reflects which threshold has been crossed |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bits) |
Data Range: |
See table below |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
The associated bit is set when the sensor reading exceed the corresponding threshold settings. |
Bit(s) |
Description |
D31:D4 |
Reserved |
D3 |
Exceeded Upper Critical Threshold |
D2 |
Exceeded Upper Warning Threshold |
D1 |
Exceeded Lower Critical Threshold |
D0 |
Exceeded Lower Warning Threshold |
Sensor Current Reading
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Reflects current reading of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents current sensor reading as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x41C6 0000 represents temperature = 24.75° Celsius. |
Sensor Minimum Reading
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Reflects minimum value of temperature sensor since power up |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents minimum sensor value as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x41C6 0000 represents temperature = 24.75° Celsius. |
Sensor Maximum Reading
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Reflects maximum value of temperature sensor since power up |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R |
Initialized Value: |
N/A |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents maximum sensor value as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x41C6 0000 represents temperature = 24.75° Celsius. |
Sensor Lower Warning Threshold
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Reflects lower warning threshold of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
Default lower warning threshold (value dependent on specific sensor) |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents sensor lower warning threshold as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0xC220 0000 represents temperature = -40.0° Celsius. |
Sensor Lower Critical Threshold
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Reflects lower critical threshold of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
Default lower critical threshold (value dependent on specific sensor) |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents sensor lower critical threshold as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0xC25C 0000 represents temperature = -55.0° Celsius. |
Sensor Upper Warning Threshold
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Reflects upper warning threshold of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
Default upper warning threshold (value dependent on specific sensor) |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents sensor upper warning threshold as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x42AA 0000 represents temperature = 85.0° Celsius. |
Sensor Upper Critical Threshold
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Reflects upper critical threshold of temperature sensor |
Type: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Data Range: |
Single Precision Floating Point Value (IEEE-754) |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
Default upper critical threshold (value dependent on specific sensor) |
Operational Settings: |
The register represents sensor upper critical threshold as a single precision floating point value. For example, for a temperature sensor, register value 0x42FA 0000 represents temperature = 125.0° Celsius. |
Ethernet Configuration Registers
Edit this on GitLab
The registers in this section provide information about the Ethernet Configuration for the two ports on the board.
Important: Regardless if the board is configured for one or two Ethernet ports, the second IP address cannot be on the same Subnet as the First IP Address. The table below provides examples of valid and invalid IP Addresses and Subnet Mask Addresses.
First Port (A) IP Address |
First Port (A) Subnet Mask |
Second Port (B) IP Address |
Second Port (B) Subnet Mask |
Result |
192.168.1.5 |
255.255.255.0 |
192.168.2.5 |
255.255.255.0 |
Good |
192.168.1.5 |
255.255.0.0 |
192.168.2.5 |
255.255.0.0 |
Conflict |
192.168.1.5 |
255.255.0.0 |
192.168.2.5 |
255.255.255.0 |
Conflict |
10.0.0.15 |
255.0.0.0 |
192.168.1.5 |
255.255.255.0 |
Good |
Ethernet MAC Address and Ethernet Settings
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Specifies the Ethernet MAC Address and Ethernet Settings for the Ethernet port. |
Type: |
Two (2) unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
See table. |
Read/Write: |
R |
Operational Settings: |
The Ethernet MAC Address consists of six octets. The Ethernet Settings are defined in table. |
Bits |
Description |
Values |
D31:D23 |
Reserved |
0 |
D22:D21 |
Duplex |
00 = Not Specified, |
D20:D18 |
Speed |
000 = Not Specified, |
D17 |
Auto Negotiate |
0 = Enabled, |
D16 |
Static IP Address |
0 = Enabled, |
Ethernet MAC Address and Ethernet Settings (Note: little-endian order in register) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 1 (Ethernet MAC Address (Octets 1-4)) (ex: aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
MAC Address Octet 4 (ex: 0xDD) |
MAC Address Octet 3 (ex: 0xCC) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
MAC Address Octet 2 (ex: 0xBB) |
MAC Address Octet 1 (ex: 0xAA) |
||||||||||||||
Word 2 (Ethernet MAC Address (Octets 5-6) and Ethernet Settings) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Ethernet Settings (See table) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
MAC Address Octet 6 (ex: 0xFF) |
MAC Address Octet 5 (ex: 0xEE) |
||||||||||||||
Ethernet Interface Name
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Specifies the Ethernet Interface Name for the Ethernet port. |
Type: |
8-character ASCII string |
Data Range: |
See table. |
Read/Write: |
R |
Operational Settings: |
The Ethernet Interface Name (eth0, eth1, etc) for the Ethernet port. |
Ethernet Interface Name (Note: little-endian order in register) (ex. “eth0”) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 1 (Bit 0-31) (ex: 0x3068 7465 = “0hte”) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
ASCII Character (ex: '0' - 0x30) |
ASCII Character (ex: 'h' - 0x68) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
ASCII Character (ex: 't' - 0x74) |
ASCII Character (ex: 'e' - 0x65) |
||||||||||||||
Word 2 (Bit 32-63) (ex: 0x0000 0000) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
ASCII Character (ex: null - 0x00) |
ASCII Character (ex: null - 0x00) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
ASCII Character (ex: null - 0x00) |
ASCII Character (ex: null - 0x00) |
||||||||||||||
Ethernet IPv4 Address
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Specifies the Ethernet IPv4 Address for the Ethernet port. |
Type: |
Three (3) unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
See table. |
Read/Write: |
R |
Operational Settings: |
The Ethernet IPv4 Address consists of three parts: IPv4 Address, IPv4 Subnet Mask and IPv4 Gateway. |
Ethernet IPv4 Address (Note: little-endian order in register) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 1 (Ethernet IPv4 Address) (ex: 0x1001 A8C0 = 192.168.1.16) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
IPv4 Address Octet 4 (ex: 0x10 = 16) |
IPv4 Address Octet 3 (ex: 0x01 = 1) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
IPv4 Address Octet 2 (ex: 0xA8 = 168) |
IPv4 Address Octet 1 (ex: 0xC0 = 192) |
||||||||||||||
Word 2 (Ethernet IPv4 Subnet) (ex: 0x00FF FFFF = 255.255.255.0) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
IPv4 Subnet Octet 4 (ex: 0x00 = 0) |
IPv4 Subnet Octet 3 (ex: 0xFF = 255) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
IPv4 Subnet Octet 2 (ex: 0xFF = 255) |
IPv4 Subnet Octet 1 (ex: 0xFF = 255) |
||||||||||||||
Word 3 (Ethernet IPv4 Gateway) (ex: 0x0101 A8C0 = 192.168.1.1) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
IPv4 Gateway Octet 4 (ex: 0x01 = 1) |
IPv4 Gateway Octet 3 (ex: 0x01 = 1) |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
IPv4 Gateway Octet 2 (ex: 0xA8 = 168) |
IPv4 Gateway Octet 1 (ex: 0xC0 = 192) |
||||||||||||||
Ethernet IPv6 Address
Edit this on GitLab
Function: |
Specifies the Ethernet IPv6 Address for the Ethernet port. |
Type: |
Five (5) unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
See table. |
Read/Write: |
R |
Operational Settings: |
The IPv6 Prefix length indicates the network portion of an IPv6 address using the following format: * IPv6 address/prefix length |
The following is an illustration of IPv6 addressing with IPv6 Prefix length of 64.
64 bits |
64 bits |
||||||
Prefix |
Interface ID |
||||||
Prefix 1 |
Prefix 2 |
Prefix 3 |
Subnet ID |
Interface ID 1 |
Interface ID 2 |
Interface ID 3 |
Interface ID 4 |
Example: 2002:c0a8:101:0:7c99:d118:9058:1235/64 |
|||||||
2002 |
C0A8 |
0101 |
0000 |
7C99 |
D118 |
9058 |
1235 |
Ethernet IPv6 Address (Note: little-endian order within 32-bit and 16-bit words in register) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 1 (Ethernet IPv6 Address (Prefix 1-2)) (ex:0xA8C0 0220 = 2002 C0A8) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Prefix 2 (ex: 0xA8C0 = C0A8) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Prefix 1 (ex: 0x0220 = 2002) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 2 (Ethernet IPv6 Address (Prefix 3/Subnet ID)) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Subnet ID (ex: 0x0000 = 0000) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Prefix 3 (ex: 0x0101 = 0101) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 3 (Ethernet IPv6 Address (Interface ID 1-2)) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Interface ID 2 (ex: 0x18D1 = D118) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Interface ID 1 (ex: 0x997C = 7C99) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 4 (Ethernet IPv6 Address (Interface ID 3-4)) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
Interface ID 4 (ex: 0x3512 = 1235) |
|||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Interface ID 3 (ex: 0x5890 = 9058) |
|||||||||||||||
Word 5 (Ethernet IPv6 Prefix Length) |
|||||||||||||||
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
Prefix Length (ex: 0x0040 = 64) |
|||||||||||||||
Interrupt Vector and Steering
Edit this on GitLab
When interrupts are enabled, the interrupt vector associated with the specific interrupt can be programmed (typically with a unique number/identifier) such that it can be utilized in the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) to identify the type of interrupt. When an interrupt occurs, the contents of the Interrupt Vector registers is reported as part of the interrupt mechanism. In addition to specifying the interrupt vector, the interrupt can be directed (“steered”) to the native bus or to the application running on the onboard ARM processor.
|
Note
|
The Interrupt Vector and Interrupt Steering registers are mapped to the Motherboard Common Memory and these registers are associated with the Module Slot position (refer to Function Register Map). |
Interrupt Vector
Function: |
Set an identifier for the interrupt. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF |
Read/Write: |
R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
When an interrupt occurs, this value is reported as part of the interrupt mechanism. |
Interrupt Steering
Function: |
Sets where to direct the interrupt. |
Type: |
unsigned binary word (32-bit) |
Data Range: |
See table Read/Write: R/W |
Initialized Value: |
0 |
Operational Settings: |
When an interrupt occurs, the interrupt is sent as specified: |
Direct Interrupt to VME |
1 |
Direct Interrupt to ARM Processor (via SerDes) (Custom App on ARM or NAI Ethernet Listener App) |
2 |
Direct Interrupt to PCIe Bus |
5 |
Direct Interrupt to cPCI Bus |
6 |
PWM Control Command Requests
Function: Provides the ability to command the onboard PWM to Reset, Power-down, or Power-up.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Operational Settings: The PWM Control Commands registers provide the ability to request the onboard PWM to perform one of the following functions - Reset, Power-down, Power-up. Only one command can be requested at a time. For example, one cannot request a Reset and a Power-down at the same time. Once the command is recognized and handled, the bit will be cleared.
|
Note
|
Clearing of the command request bit only indicates the command has been recognized and initiated, it does not indicate that the command action has been completed. There is one Control Command Request register. The register is Bit-mapped as shown in the table below: |
Bit(s) |
Description |
D31:D3 |
Reserved |
D2 |
PWM Power-up |
D1 |
PWM Power-down |
D0 |
PWM Reset |
PWM Health Monitoring Registers
PWM Communications Status
Function: Provides the ability to monitor factors that may affect the communication status of the PWM.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Operational Settings: The PWM Communications register provide the ability to monitor factors that may affect the Communications Status of the onboard PWM. Each communication factor is bit mapped to the register as shown in the table below:
Bit(s) |
Description |
D31:D5 |
Reserved |
D4 |
PWM Communications Error Detected |
D3 |
PWM Firmware Not Ready |
D2 |
PWM LinkInit Not Done |
D1 |
PWM Not Detected |
D0 |
PWM Powered-down |
PWM Powered-down: The user can request the onboard PWM be powered-down (see PWM Control Command Requests). Once the request is detected and acted upon, this bit will be set. Once powered-down, you will not be able to communicate with the PWM.
PWM Not Detected: If the onboard PWM has not been detected, you will not be able to communicate with the PWM.
PWM LinkInit Not Done: PWM communications is accomplished via SERDES. LinkInit is required to establish a connection to the onboard PWM. If the LinkInit has not been successfully completed, you will not be able to communicate with the PWM.
PWM Firmware Not Ready: The onboard PWM has Firmware that is ready from PWM QSPI and loaded for execution. If this Firmware was not loaded and started successfully, you may not be able to communicate with the PWM.
PWM Communications Error Detected: If at some point during run-time, communications with the onboard PWM have failed, this bit will be set.
PWM BIT Status
Function: Provides the ability to monitor the onboard PWM BIT Status.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Operational Settings: The PWM BIT Status registers provide the ability to monitor the onboard PWM BIT results as Latched and current value. A 1 is any bit field indicates BIT failure for the PWM.
Bit(s) |
Description |
D31:D18 |
Reserved |
D17 |
PWM BIT Failure (current value) |
D16 |
Reserved |
D15:D2 |
Reserved |
D1 |
PWM BIT Failure - Latched |
D0 |
Reserved |
MOTHERBOARD FUNCTION REGISTER MAP
Key:
Bold Underline = Measurement/Status/Board Information
Bold Italic = Configuration/Control
PWM Information Registers
0x03FC |
PWM Addressing Ready |
R |
0x0400 |
PWM Address |
R |
0x0430 |
PWM Size |
R |
0x0460 |
PWM ID |
R |
Hardware Information Registers
0x0020 |
Product Serial Number |
R |
0x0024 |
Platform |
R |
0x0028 |
Model |
R |
0x002C |
Generation |
R |
0x0030 |
Processor Count/Ethernet Count |
R |
0x0034 |
Maximum Module Slot Count/ARM Platform Type |
R |
Motherboard Firmware Information Registers
Motherboard Core Information
0x0100 |
MBCore Major/Minor Version |
R |
0x0104 |
MBCore Minor 2/3 Version |
R |
0x0108 |
MBCore Build Date |
R |
Motherboard FPGA Information
0x0270 |
MB FPGA Revision |
R |
0x0274 |
MB FPGA Compile Date/Time |
R |
Motherboard Monitoring Registers
Temperature Readings
0x0200 |
Current Zynq Temperatures |
R |
0x0204 |
Reserved |
R |
0x0208 |
Max Zynq Temperatures |
R |
0x020C |
Reserved |
R |
0x0210 |
Min Zynq Temperatures |
R |
0x0214 |
Reserved |
R |
Higher Precision Temperature Readings
0x0230 |
Current Zynq Core Temperature |
R |
0x0234 |
Current Motherboard PCB Temperature |
R |
Ethernet Configuration Registers
0x0070 |
Ethernet A MAC (Octets 1-4) |
R |
0x0074 |
Ethernet A MAC (Octets 5-6)/Misc Settings |
R |
0x0078 |
Ethernet A Interface Name (Bit 0-31) |
R |
0x007C |
Ethernet A Interface Name (Bit 32-63) |
R |
0x0080 |
Ethernet A IPv4 Address |
R |
0x0084 |
Ethernet A IPv4 Subnet Mask |
R |
0x0088 |
Ethernet A IPv4 Gateway |
R |
0x008C |
Ethernet A IPv6 Address (Prefix 1-2) |
R |
0x0090 |
Ethernet A IPv6 Address (Prefix 3/Subnet ID) |
R |
0x0094 |
Ethernet A IPv6 Address (Interface ID 1-2) |
R |
0x0098 |
Ethernet A IPv6 Address (Interface ID 3-4) |
R |
0x009C |
Ethernet A IPv6 Prefix Length |
R |
0x00A0 |
Ethernet B MAC (Octets 1-4) |
R |
0x00A4 |
Ethernet B MAC (Octets 5-6)/Misc Settings |
R |
0x00A8 |
Ethernet B Interface Name (Bit 0-31) |
R |
0x00AC |
Ethernet B Interface Name (Bit 32-63) |
R |
0x00B0 |
Ethernet B IPv4 Address |
R |
0x00B4 |
Ethernet B IPv4 Subnet Mask |
R |
0x00B8 |
Ethernet B IPv4 Gateway |
R |
0x00BC |
Ethernet B IPv6 Address (Prefix 1-2) |
R |
0x00C0 |
Ethernet B IPv6 Address (Prefix 3/Subnet ID) |
R |
0x00C4 |
Ethernet B IPv6 Address (Interface ID 1-2) |
R |
0x00C8 |
Ethernet B IPv6 Address (Interface ID 3-4) |
R |
0x00CC |
Ethernet B IPv6 Prefix Length |
R |
Interrupt Vector and Steering
0x0500 – 0x057C |
PWM Interrupt Vector 1 - 32 |
R/W |
0x0600 – 0x067C |
PWM Interrupt Steering 1 - 32 |
R/W |
PWM CARD REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
Board Information Registers
The registers identified in this section provide information about the PWM’s FPGA revision.
FPGA Revision
Function: Specifies the major and minor revision of the FPGA.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: N/A.
Operational Settings: The upper byte equals the Major Revision. The lower byte equals the Minor Revision. Example: 0x0202 = rev 2.2.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Major Revision |
Minor Revision |
||||||||||||||
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
FPGA Sub-Revision
Function: Specifies the sub-revision of the FPGA.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: N/A
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
PWM Standard Operation Registers
The registers identified in this section provide information about PWM Channel Control, DAC Control, ADC Control, Measurement and Status Registers.
PWM Channel Control Registers
Current Command
Function: Latches its value to the drive command when the module is operating in current mode.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0xF800 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: The command is a 12-bit signed integer and is mapped into the LSB’s of a 16-bit register with sign bit extension.
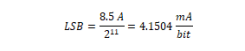
Minimum value |
F800: -8.500A |
Maximum value |
07FF: +8.496A |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Voltage Command
Function: Latches its value to the drive command when the module is operating in voltage mode.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0xF800 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: The command is a 12-bit signed integer and is mapped into the LSB’s of a 16-bit register with sign bit extension.
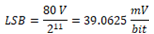
Minimum value |
F800: -80.000V |
Maximum value |
07FF: +79.961V |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Drive Enable
Function: Provides enable/disable control of the channel output stage.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000 (disabled)
Operational Settings: N/A
Drive enabled/disabled |
0000: Drive disabled Other: Drive enabled |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
writing to the Drive Reset register does NOT clear this register |
Drive Reset
Function: Used to clear all fail conditions related to the channel output in the Status Register.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000 (inactive)
Operational Settings: N/A
Drive reset |
0000: Reset inactive Other: Reset active |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
A write to this register is not latched. The register will be cleared to its default value after a successful write. |
|
Note
|
A write to this register does not modify the Drive Enable register. |
|
Note
|
in the event of a shut-down fault condition the channel will be disabled. To restore normal operation, write the appropriate value to this register. If on-board faults are resolved, normal operation will be restored. |
DAC Control
DAC Test Word 1
Function: Provides bus read access to the RS-422 SDLC receive date for DAC test word #1.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0xF800 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Minimum value |
F800: -2048 (-10V) |
Maximum value |
07FF: 2047 (9.995V) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
If no test word is transmitted or if an error is detected in the SDLC data frame, the last valid test word value will be output. |
|
Note
|
This test word is output on DAC channel #1 or TST-WRD1 (P1.B6 and JP4.14). |
DAC Test Word 2
Function: Provides bus read access to the RS-422 SDLC receive date for DAC test word #2.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0xF800 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Minimum value |
F800: -2048 (-10V) |
Maximum value |
07FF: 2047 (9.995V) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
If no test word is transmitted or if an error is detected in the SDLC data frame, the last valid test word value will be output. |
|
Note
|
This test word is output on DAC channel #2 or TST-WRD2 (P1.C6 and JP4.15). |
ADC Control
ADC Test Input
Function: Provides bus read access to channel 1 of the debug ADC.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0xF800 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Minimum value |
F800: -10.24V on the ADC input |
Maximum value |
07FF: +10.24V on the ADC input |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
ADC Test Input Channels 1-4
Function: Provides bus read access to channels 1-4 of the debug ADC.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0xF800 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Minimum value |
F800: -10.24V on the ADC input |
Maximum value |
07FF: +10.24V on the ADC input |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
ADC Test Input Channel 1 register is the same as ADC Test Input register. |
ADC Input Enable
Function: Enables or disables the ADC input test for either transmission over the RS-422 SDLC interface or injection into the PWM module channel control loop summoning junctions.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Destination of the ADC input is determined by the ADC Input Destination Select register.
ADC Input enable |
FFFF: ADC input enabled Other: ADC input disabled |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
ADC Input Destination Select
Function: Selects the destination for the ADC Test Input Word.
Type: other
Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: The available destinations are either RS-422 SDLC interface or the summing junctions of the PWM Channel Loop Controllers. The purpose of this register is to allow lab analysis of the PWM loop controller for verification purposes of the loop characteristics.
ADC Input destination select |
0000: ADC input is transmitted over SDLC 5555: ADC input is summed into Ch 1 loop Other: Invalid |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
Only channel 1 of the ADC debug input is fed into the summing junction of the current loop. Its value can be read at the ADC Test Input Channel 1 register. |
Measurement Registers
Drive Current Measurement
Function: Contains the measured motor current value.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0xF800 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Overflow or underflow values shall be clamped at the maximum positive or negative values.
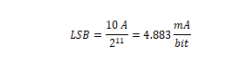
Minimum value |
F800: -10.00A |
Maximum value |
07FF: +9.995A |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Drive Voltage Measurement
Function: Contains the measured motor voltage value.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0xF800 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Overflow or underflow values shall be clamped at the maximum positive or negative values.
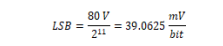
Minimum value |
F800: -80.000V |
Maximum value |
07FF: +79.961V |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Drive Temperature
Function: Reports the temperature of the output drive stage.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x8000 to 0x7FFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
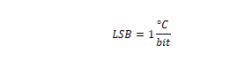
Minimum value |
8000: -32768 ºC |
Maximum value |
7FFF: +-32767 ºC |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Measured Supply Voltage
Function: Contains the measured +65V onboard supply voltage value.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0x07FF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Overflow or underflow values shall be clamped at the maximum positive or negative values.
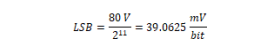
Minimum value |
0000: 0.000V |
Maximum value |
07FF: +79.961V |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Measured Supply Current
Function: Contains the measured current of the +65V onboard supply.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0x0FFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
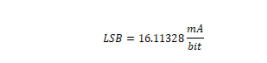
Minimum value |
0000: 0.000 A |
Maximum value |
07FF: +65.984 A |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Measured Input Voltage
Function: Contains the measured voltage of the external supply to the card.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0x0FFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
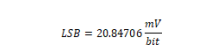
Minimum value |
0000: 0.000V |
Maximum value |
0FFF: +85.369V |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
PS Temperature
Function: Reports the temperature of the on-board power supply.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x8000 to 0x7FFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
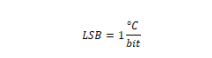
Minimum value |
8000: -32768 ºC |
Maximum value |
7FFF: +-32767 ºC |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
PWM Duty Limit
Function: Defines the maximum and minimum values the output state PWM duty cycle is saturated to.
Type: integer
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0x03FF (0 to 1023)
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x03B6 (950)
Operational Settings: N/A
Minimum value |
0000: 50% low & 50% high |
Maximum value |
03FF: 0% low and 100% high |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Elapsed Time Counter Hi
Function: Upper word of the on-board elapsed time counter.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: N/A.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Elapsed Time Counter Lo
Function: Lower word of the on-board elapsed time counter.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: N/A.
Operational Settings: This register and Elapsed Time Counter Hi represent the total 'on' time of the PWM card.
LSB=0.250 s |
Example: 0x0120 = 0x0001 0x0124 = 0x3251 Time = 0x0001 3251 = 78417 * 0.25s = 19604.25s |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Status Registers
Status Register
Function: Sets the corresponding bit associated with the channel’s General Interrupt status.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
D31:D16 |
Reserved |
D15 |
Master drive switch 0. Enabled (switch closed) 1. Disabled (switch open) |
D14 |
Battlefield Override 0. Enabled 1. Disabled |
D13* |
Channel 1 drive fault 0. Normal 1. Active |
D12 |
PS Current Limited 0. Normal 1. Current mode |
D11:D10 |
Reserved |
D9 |
Channel 1 overcurrent 0. Normal 1. Active |
D8 |
Bus Watchdog 0. Normal 1. Fault |
D7 |
SDLC Watchdog 0. Normal 1. Fault |
D6:D5 |
Reserved |
D4 |
PS Over Temperature 0. Normal 1. Fault |
D3 |
Reserved |
D2 |
Drive Over Temperature 0. Normal 1. Fault |
D0 |
PS Overvoltage 0. Normal 1. Active |
|
Note
|
*This status bit is latched until a reset is performed (Soft Reset or Drive Reset) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
0 |
0 |
D |
D |
D |
0 |
0 |
D |
0 |
D |
D |
D |
Latched Status Register
Function: Sticky status bit register.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
|
Note
|
Same as Status Register (see that register for bit descriptions). |
Clear Latched Status Register
Function: Implements a non-latched reset of the Latched Status Register.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Clear latched status register |
0000: Inactive Other: Clear latched status register |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
The register will be cleared to its default value after a successful write. |
Board Ready
Function: Reports when the board is ready for communication.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 or 0xAA55.
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000 (not ready)
Operational Settings: N/A
Board Ready |
0000: Board not ready AA55: Board ready |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Software Init Done
Function: Reports when the board software is ready for operation.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 or 0x0001.
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000 (not ready)
Operational Settings: N/A
Board Ready |
0000: Not ready 0001: Ready |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Log Data Register
Function: Provides fault log data.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Register functionality outlined in Appendix.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Log Control Register
Function: Provides access to the fault log.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Register functionality outlined in Appendix.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
PWM Configuration Registers
The registers in this section provide information on the PWM configuration, channel configuration, and bus watchdog registers.
PWM Configuration Registers
Mode Select
Function: Selects the definition of the motor drive topology.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Mode select |
0000: Current mode Other: Voltage mode |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Command Source Select
Function: Selects the source of the motor current/voltage commands.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Command source select |
0000: RS-422 SDLC interface Other: Bus interface (PCIe or ETH) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Channel Configuration
Current Limit
Function: Controls the maximum allowable current sourced by the output.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0x7FFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Negative values are latched as a value of zero.
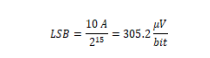
Minimum value |
0000: 0.000A |
Maximum value |
7FFF: 9.995A |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
The current limit defaults to 1A to prevent overcurrent faults on the Status Register triggered by noise on the measurement. |
Kc Gain
Function: Specifies the 16-bit input command scaling gain.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x8000 to 0x7FFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Maximum negative value |
8000: -1 (scaling) |
Maximum positive value |
7FFF: +1 (scaling) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
NOTE The gain is treated as a signed integer. Setting a negative gain value will result in the polarity reversal of the command.
Kg Gain
Function: Specifies the 16-bit global gain.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x8000 to 0x7FFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Maximum negative value |
8000: -10 (scaling) |
Maximum positive value |
7FFF: +10 (scaling) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
The gain is treated as a signed integer. Setting a negative gain value will result in the polarity reversal of the error term. |
Ki Gain
Function: Specifies the 16-bit integral gain.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x8000 to 0x7FFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Maximum negative value |
8000: -1 (scaling) |
Maximum positive value |
7FFF: +1 (scaling) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
The gain is treated as a signed integer. Setting a negative gain value will result in the polarity reversal of the command. |
|
Note
|
The integral term is driven by the sample rate of the current measurements: |
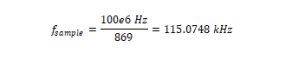
Kp Gain
Function: Specifies the 16-bit proportional gain.
Type: signed binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x8000 to 0x7FFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Maximum negative value |
8000: -2 (scaling) |
Maximum positive value |
7FFF: +2 (scaling) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
The gain is treated as a signed integer. Setting a negative gain value will result in the polarity reversal of the error term. |
Bus Watchdog Registers
Bus Watchdog Enable
Function: Provides enable or disable control of the bus activity watchdog.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
Bus watchdog enable |
FFFF: Enabled Other: Disabled |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Bus Watchdog Timer Status
Function: Displays the status of the watchdog timer.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x1234 or 0xAAAA
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: A watchdog failure condition will latch the failure value. The watchdog fault can be cleared via a power cycle of the card or a toggle of the Bus Watchdog Enable register.
Watchdog timer status |
AAAA: Watchdog timeout 1234: Watchdog disabled or healthy |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Bus Watchdog Period
Function: Provides the capability to define the watchdog timer interval for a bus activity monitor.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: If the Status Register is not accessed via successful write within the defined interval, the PWM card shall disable both output channels (regardless of battlefield override state).
Bus watchdog period |
0000: 0 milliseconds FFFF: 250 milliseconds |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
General Control Registers
The registers in this section provide information on the soft reset, battlefield override and power supply control registers.
Soft Reset
Function: Disables the PWM card’s current controller functionality.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Both the drive PWMs and fault reporting are disabled. During rest, read/writes to the defined registers are still possible.
Soft reset |
0000: Reset inactive Other: Reset active |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
Taking the controller OUT of soft reset will set all defined registers to their DEFAULT values. |
Battlefield Override
Function: Used to lockout all fail-safes (except communication watchdogs) within the PWM card.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: When active, intervention of the protection circuitry to shut the drives off to either PWM channel is NOT allowed (except for Watchdog timers). The status of any protection logic is still updated within the Status Register to indicate a failure exists.
Battlefield override |
0000: Override inactive Other: Override active |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Disable PS Over-Temperature Shutdown
Function: Allows the user to disable the power supply ‘over-temperature' protection on the card.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: If a PS over-temperature fault is detected, the drive stage will be disabled.
Disable PS Over-Temperature Shutdown |
FFFF: Protection disabled Other: Protection enabled |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
PS Reenable
Function: Allows the user to re-enable the power supply after a fault.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: If a PS Overtemp fault occurs (in Status Register) the on-board PS will shut down unless BATTLEFIELD OVERRIDE or DISABLE_PS_OT_SHUTDOWN is set. This shutdown is a latched condition. Write to the PS_REENABLE register to re enable the PS after a fault.
Disable PS Over-Temperature Shutdown |
0000: Inactive Other: Re-enable after fault |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
The register will be cleared to its default value after a successful write. |
PWM Serial Registers
SDLC Edge Select
Function: Allows the user to select the clock edge used by the RS-422 SDLC serial port.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Transmit and receive functions will use opposite edges as defined below.
SDLC Edge Select |
0000: Rx falling edge, Tx rising edge Other: Tx falling edge, Rx rising edge |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
CRC Error and Data Frame Registers
SDLC Total CRC Errors
Function: Captures RS-422 SDLC Receive Data Frame CRC errors.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: Whenever a CRC error is detected within a received data frame this register will increment its value. The maximum value is 65535.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
The counter will stop (and not rollover) when its maximum value is reached. The counter is reset by the SDLC Clear CRC Errors register. |
SDLC Total Data Frames
Function: Captures the number of RS-422 SDLC Receive Data Frames received (valid or invalid).
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: The maximum value is 65535.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
|
Note
|
The counter will stop (and not rollover) when its maximum value is reached. The counter is reset by the SDLC Clear Data Frames register. |
SDLC Clear CRC Errors
Function: Clears the RS-422 SDLC CRC error counter in the SDLC Total CRC Errors register.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: While this register is in the inactive state, the error count register is allowed to increment. When the active state is commanded the error count register shall clear its count value to 0000 and refrain from incrementing its error count.
SDLC clear CRC errors |
0000: Reset inactive Other: Reset active |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
SDLC Clear Data Frames
Function: Clears the number of RS-422 SDLC data frames received in the SDLC Total Data Frames register.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: While this register is in the inactive state, the error count register is allowed to increment. When the active state is commanded the count register shall clear its count value to 0000 and refrain from incrementing its error count.
SDLC clear data frames |
0000: Reset inactive Other: Reset active |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
SDLC Last Data Frame Status
Function: Indicates the status of the last RS-422 SDLC data frame received.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0000 or 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: If a data frame is interrupted for any reason, an error indication shall be indicated within this register. This register shall retain the status of the last data frame received until another data frame transmission has completed and new status is available to update this register value.
SDLC last data frame status |
FFFF: Error detected on last RS-422 SDLC data frame 0000: No error detected on last RS-422 SDLC data frame |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Serial Test Registers
SDLC RS422 Test Bits
Function: Bits to be transmitted in the last Tx SDLC data frame if test bits are enabled.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x0 to 0xF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0
Operational Settings: Test bits are enabled via the SDLC Tx Message Configuration register.
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
SDLC RS422 Transmit Enable
Function: Enables SDLC transmission of a frame after receipt of a valid frame.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
SDLC RS422 transmit enable |
0000: Disables SDLC transmission Other: Enables SDLC transmission |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
SDLC Tx Message Configuration
Function: Configures the behavior of the last byte of the Tx Data Frame.
Type: boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: The last byte may represent either the test bits defined in the SDLC RS422 Test Bits register or the following Status Register bits.
SDLC Tx message configuration |
0000: Test bits Other: STATUS register bits |
D3 |
PS overvoltage or undervoltage (Status Register D1 or D0) |
D2 |
'0' |
D1 |
Drive 1 fault (Status Register D13) |
D0 |
Master drive switch status for D0 (Status Register D15) |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Serial Watchdog Registers
SDLC Timeout Period
Function: Provides the capability to define the watchdog timer interval for a SDLC activity monitor.
Type: unsigned binary word (32-bit)
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: If a valid data frame is not received within the defined interface, the PWM card shall disable both output channels (regardless of battlefield override state).
SDLC watchdog period |
0000: 0 milliseconds FFFF: 250 milliseconds |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
SDLC Watchdog Timer Enable
Function: Provides enable or disable control of the RS-422 SDLC activity watchdog.
Type: Boolean
Data Range: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: N/A
SDLC watchdog timer enable |
0000: Watchdog disabled Other: Watchdog enabled |
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
SDLC Watchdog Timer Status
Function: Displays the status of the watchdog timer.
Type: other
Data Range: 0x1234 or 0xAAAA
Read/Write: R/W
Initialized Value: 0x0000
Operational Settings: A watchdog failure condition will latch the failure value. The watchdog fault can be cleared via a power cycle of the card or a toggle of the SDLC Watchdog Timer Enable register.
| SDLC watchdog timer status | AAAA: Watchdog timeout |
|---|
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Test Registers
Read Only Test Register
Function: A read-only register used to test the communication link.
Type: N/A
Data Range: 0x1122 AABB
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x1122 AABB
Operational Settings: N/A
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
Read/Write Test Registers
Function: A read/write register used to test the communication link.
Type: N/A
Data Range: 0x0000 0000 to 0xFFFF FFFF
Read/Write: R
Initialized Value: 0x8899 EEFF
Operational Settings: N/A
D31 |
D30 |
D29 |
D28 |
D27 |
D26 |
D25 |
D24 |
D23 |
D22 |
D21 |
D20 |
D19 |
D18 |
D17 |
D16 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D15 |
D14 |
D13 |
D12 |
D11 |
D10 |
D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
D |
PWM FUNCTION REGISTER MAP
Key:
Bold Underline = Measurement/Status/Board Information
Bold Italic = Configuration/Control
PWM Standard Operation Registers
PWM Channel Control Registers
0x000C |
Current Command |
R/W |
0x0010 |
Voltage Command |
R/W |
0x0008 |
Drive Enable |
R/W |
0x0020 |
Drive Reset |
R/W |
DAC Control Registers
0x00A0 |
DAC Test Word 1 |
R |
0x00A4 |
DAC Test Word 2 |
R |
ADC Control Registers
0x00A8 |
ADC Test Input |
R |
0x0200 |
ADC Test Input Ch 1 |
R |
0x0204 |
ADC Test Input Ch 2 |
R |
0x0208 |
ADC Test Input Ch 3 |
R |
0x020C |
ADC Test Input Ch 4 |
R |
0x00AC |
ADC Input Enable |
R/W |
0x00B0 |
ADC Input Destination Select |
R/W |
Measurement Registers
0x0018 |
Drive Current Measurement |
R |
0x001C |
Drive Voltage Measurement |
R |
0x00E0 |
Drive Temperature |
R |
0x008C |
Measured Supply Voltage |
R |
0x0140 |
Measured Supply Current |
R |
0x0144 |
Measured Input Voltage |
R |
0x00E8 |
PS Temperature Measurement |
R |
0x00EC |
PWM Duty Limit |
R/W |
0x0120 |
Elapsed Time Counter Hi |
R |
0x0124 |
Elapsed Time Counter Lo |
R |
Status Registers
0x009C |
Status Register |
R |
0x0138 |
Latched Status Register |
R |
0x013C |
Clear Latched Status Register |
R/W |
0x01FC |
Board Ready |
R |
0x02FC |
SW Init Done |
R |
0x01E8 |
Log Data Register |
R |
0x01EC |
Log Control Register |
R/W |
PWM Configuration Registers
PWM Configuration Registers
0x0000 |
Mode Select |
R/W |
0x0004 |
Command Source Select |
W |
Channel Configuration Registers
0x0014 |
Current Limit |
R/W |
0x004C |
Kc Gain |
R/W |
0x0050 |
Kg Gain |
R/W |
0x0054 |
Ki Gain |
R/W |
0x005C |
Kp Gain |
R/W |
Bus Watchdog Registers
0x00B4 |
Bus Watchdog Enable |
R/W |
0x00F8 |
Bus Watchdog Timer Status |
R |
0x00BC |
Bus Watchdog Period |
R/W |
General Control Registers
0x00C4 |
Soft Reset |
R/W |
0x0098 |
Battlefield Override |
R/W |
0x00F4 |
Disable PS Over-Temperature Shutdown |
R/W |
0x0160 |
PS Reenable |
R/W |
PWM Serial Registers
0x0074 |
SDLC Edge Select |
R/W |
CRC Error and Data Frame Registers
0x0078 |
SDLC Total CRC Errors |
R |
0x007C |
SDLC Total Data Frames |
R |
0x0080 |
SDLC Clear CRC Errors |
R/W |
0x0084 |
SDLC Clear Data Frames |
R/W |
0x0088 |
SDLC Last Data Frame Status |
R |
Serial Test Registers
0x0090 |
SDLC RS422 Test Bits |
R/W |
0x0094 |
SDLC RS422 Transmit Enable |
R/W |
0x0110 |
SDLC Tx Message Configuration |
R/W |
Serial Watchdog Registers
0x00C0 |
SDLC Timeout Period |
R/W |
0x00B8 |
SDLC Watchdog Timer Enable |
R/W |
0x010C |
SDLC Watchdog Timer Status |
R |
ETHERNET
Edit this on GitLab
(For detailed supplement, please visit the NAI web-site specific product page and refer to: Ethernet Interface for Generation 5 SBC and Embedded IO Boards Specification)
|
Note
|
For products capable of 10/100/1000Base-KX functionality – the product Ethernet PHY supports 1000BASE-X. Product interoperability with 10/100/1000BASE-KX is supported with 1000BASE-X (provided that auto-negotiation is disabled). |
The Ethernet Interface Option allows communications and control access to all function modules either via the system BUS or Ethernet ports 1 or 2.
Ethernet 1 |
Ethernet 2 |
Ethernet 3* |
Ethernet 4* |
|
(REF PORT A) |
(REF PORT B) |
(REF PORT C) |
(REF PORT D) |
|
The default IP address: |
192.168.1.16 |
192.168.2.16 |
192.168.3.16 |
192.168.4.16 |
The default subnet: |
255.255.255.0 |
255.255.255.0 |
255.255.255.0 |
255.255.255.0 |
The default gateway: |
192.168.1.1 |
192.168.2.1 |
192.168.3.1 |
192.168.4.1 |
*see Part Number Designation for applicability.
|
Note
|
Actual "as shipped" card Ethernet default IP addresses may vary based upon final ATP configuration(s). |
The NAI interface supports IPv4 and IPv6 and both the TCP and UDP protocols. The Ethernet Operation Mode Command Listener application running on the motherboard host processor implements the operation interface. The listener is operational on startup through the nai_MBStartup process and listen on specific ports for commands to process. The default ports are listed below:
-
TCP1 - Port 52801
-
TCP2 - Port 52802
-
UDP1 - Port 52801
-
UDP2 - Port 52802
While the listener is active, note that interrupts from the motherboard do not trigger. The listener can be disabled by turning off the nai_MBStartup process through the Motherboard EEPROM. To turn off nai_MBStartup use the command mbeeprom_util set MBStartupInitOnlyFlag 1 in the console, either by serial port or telnet to the motherboard, and then reboot the system. To turn on the nai_MBStartup use the command mbeeprom_util set MBStartupInitOnlyFlag 0 in the console, either by serial port or telnet to the motherboard, and then reboot the system.
Ethernet Message Framework
The interface uses a specific message framework for all commands and responses. All messages begin with a Preamble code and end with a Postamble code. The message framework is shown below.
|
Preamble 2 bytes Always 0xD30F |
SequenceNo 2 bytes |
Type Code 2 byte |
Message Length (2 bytes) |
Payload (0..1414 bytes) |
Postamble 2 bytes Always 0xF03D |
Message Elements
Preamble |
The Preamble is used to delineate the beginning of a message frame. The Preamble is always 0xD30F. |
SequenceNo |
The SequenceNo is used to associate Commands with Responses. |
Type Code |
Type Codes are used to define the type of Command or Response the message contains. |
Message Length |
The Message Length is the number of bytes in the complete message frame starting with and including the Preamble and ending with and including the Postamble. |
Payload |
The Payload contains the unique data that makes up the command or response. Payloads vary based on command type. |
Postamble |
The Postamble is use to delineate the end of a message frame. The Postamble is always 0xF03D. |
Notes
-
The messaging protocol applies only to card products.
-
Messaging is managed by the connected (client) computer. The client computer will send a single message and wait for a reply from the card. Multiple cards may be managed from a single computer, subject to channel and computer capacity.
Board Addressing
The interface provides two main addressing areas: Onboard and Off-board.
Onboard addressing refers to accessing resources located on the board that is implementing the operation interface (including its modules).
Off-board addressing refers to accessing resources located on another board reachable via VME, PCI, or other bus. Off-board addressing requires a Master/Slave configuration.
The user must always specify if a particular address is Onboard or Off-board. See the command descriptions for the onboard and off-board flags.
Within a particular board (Onboard or Off-board), the address space is broken up into two areas: Motherboard Common Address Space and Module Address Space. All addresses are 32-bit.
Motherboard Common Address Space starts at 0x00000000 and ends at 0x00004000. This is a 4Kx32-bit address space (16 kbytes).
Module Address Space starts at 0x00004000. Module addressing is dynamically configured at startup. NAI boards support between 1 and 6 modules. The minimum module address space size is 4Kx32 (16 kbytes) and module sizes are always a multiple of 4Kx32.
Module addressing is dynamic and cumulative. The first detected module (starting with Slot 1) is given an address of 0x00004000. The 2nd detected Module is given an address of:
First_Detected_Module_Address + First_Detected_Module_Size
|
Note
|
Slots do not define addresses. |
If no module is detected in a module slot, that slot is not given an address. Therefore, if the first detected Module is in Slot 2, then that module address will be 0x00004000. If the next detected module is in Slot 4, then the address of that Module will be:
Second_Detected_Module_Address = First_Detected_Module_Address + First_Detected_Module_Size
If a 3rd Module is detected in Slot 6, then the address of that Module will be:
Third_Detected_Module_Address = Second_Detected_Module_Address + Second_Detected_Module_Size
|
Note
|
Module addresses are calculated at each board startup when the modules are detected. Therefore, if a module should fail to be detected due to malfunction or because it was removed from the motherboard, the addresses of the modules that follow it in the slot sequence will be altered. This is important to note when programming to this interface. |
Users can always retrieve the Module Addresses, Module Sizes and Module IDs from the fixed Motherboard Common address area. This data is set upon each board startup. While the Module Addressing is dynamic, the address where these addresses are stored is fixed. For example, to find the startup address of the module location in Slot 3, refer to the MB Common Address 0x00000408 from the Motherboard Common Addresses table that follows.
Ethernet Wiring Convention
RJ-45 Pin |
T568A Color |
T568B Color |
10/100Base-T |
1000BASE-T |
NAI wiring convention |
1 |
white/green stripe |
white/orange stripe |
TX+ |
DA+ |
ETH-TP0+ |
2 |
green |
orange |
TX- |
DA- |
ETH-TP0- |
3 |
white/orange stripe |
white/green stripe |
RX+ |
DB+ |
ETH-TP1+ |
4 |
blue |
blue |
DC+ |
ETH-TP2+ |
|
5 |
white/blue stripe |
white/blue stripe |
DC- |
ETH-TP2- |
|
6 |
orange |
green |
RX- |
DB- |
ETH-TP1- |
7 |
white/brown stripe |
white/brown stripe |
DD+ |
ETH-TP3+ |
|
8 |
brown |
brown |
DD- |
ETH-TP3- |
68PW1 CONNECTOR/PIN-OUT INFORMATION
The 68PW1 3U OpenVPX single-axis PWM servo motor drive is available in one configuration: conduction-cooled. The 68PW1 follows the OpenVPX “Payload Slot Profile” configured as:
Slot profile: SLT3-PER-2U2U-14.2.17
Module profile: MOD3-PER-2U2U-16.2.16-1
User I/O is available through the OpenVPX user defined rear I/O connector P1 (see part number and pin-out information).
Notes
The following notes apply unless otherwise specified:

Front Panel Utility Connector JP4 (Conduction-Cooled)
The 68PW1 utilizes a Mini-HDMI type card edge connector JP4, available on conduction-cooled configurations that provides the following signals:
-
Serial (port 1)
-
Ethernet port 1 (factory configuration option)
-
ADC debug
-
DAC debug outputs
-
TST-WRD1
-
TST-WRD2
-
PWM-CMD1 (Drive 1 Current)
-
NAI also provides an optional “breakout” adapter board (NAI P/N 68PW1-ADPT-ETH-SER-AD-DA) with a mini-HDMI to mini-HDMI type cable. The “breakout” adapter board and a Micro-HDMI cable (NAI P/N 75SBC4-BB) allow for standard I/O connections to Ethernet and asynchronous serial (DB9). Consult the factory for availability.
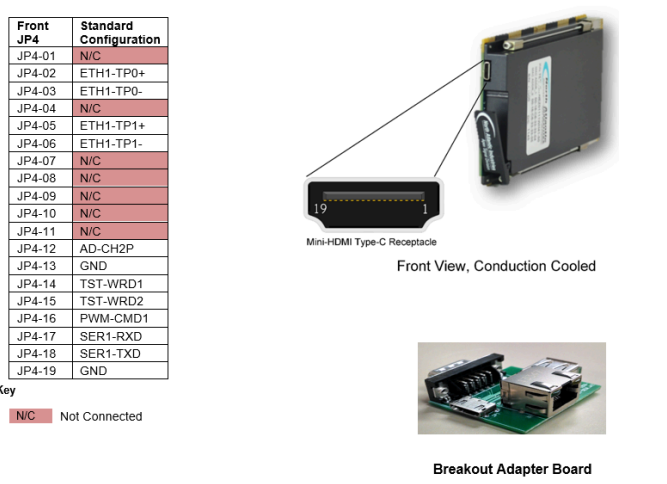
Signal Descriptions JP4
Signal Name |
Description |
ETH1-TPx |
Ethernet port 1 signals (2 pair) 10/100 twisted pair signals (Optional) |
AD-CH2P |
Input to channel 2 of the debug ADC |
TST-WRD1 |
Debug DAC output of test word #1 (from SDLC) |
TST-WRD2 |
Debug DAC output of test word #2 (from SDLC) |
PWM-CMD1 |
Debug DAC output of the Drive Current |
SER1-TXD |
Asynchronous transmit serial data port 1 (out) / RS232 debug/console port only |
SER1-RXD |
Asynchronous received serial data port 1 (in) / RS232 debug/console port only |
GND |
System Ground (return) |
Rear I/O VPX Connectors P0-P3 (Conduction-Cooled)
The 68PW1 3U OpenVPX single-axis PWM servo motor drive provides interface via the rear VPX connectors.
Rear I/O Summary
Signals defined as N/C currently have no functionality associated and are not required for general operation.
P0 - Utility plane. Contains the following signal definitions: |
|
Power: |
Primary +12V, +3.3_AUX, +/- 12V_AUX and System GND |
Geographical Address Pins: |
GA0# - GA4#, GAP# |
Card reset: |
SYSRST# signal |
VPX AUX/REF CLK |
(Not used) |
P1 - Defined as primarily Data/Control Planes (User defined I/O secondary) |
|
High Speed Switched Fabric Interface: |
One ultra-thin pipe option (PCIe ver. 2.0 (x1)). |
Ethernet: |
1000Base-KX |
P2 - Motor Drive Output/Power RTN |
Input source return Motor power output |
P3 - PWM/Drive |
+28VDC input source |
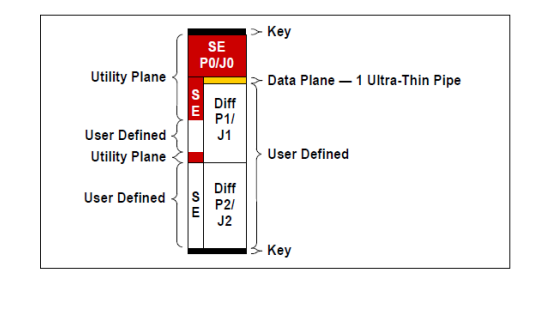
Rear I/O Utility Plane (P0)
The P0 (Utility) Plane contains the primary power, bus, and utility signals for the OpenVPX board. Additionally, several of the user defined pins can be utilized for Geographical Addressing and a parallel SYSRST# signal. Signals defined as N/C currently have no functionality associated and is not required for general operation.
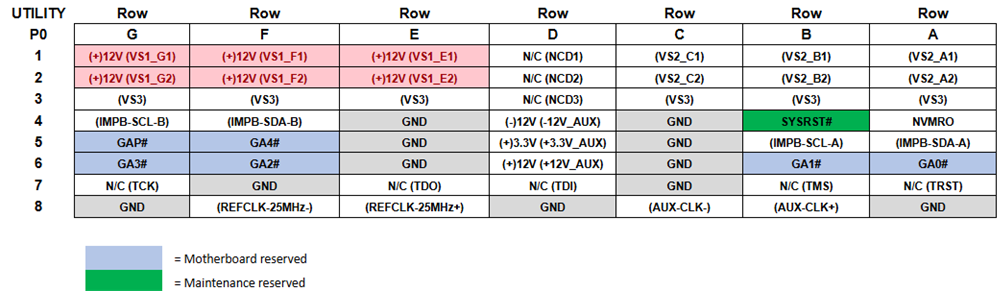
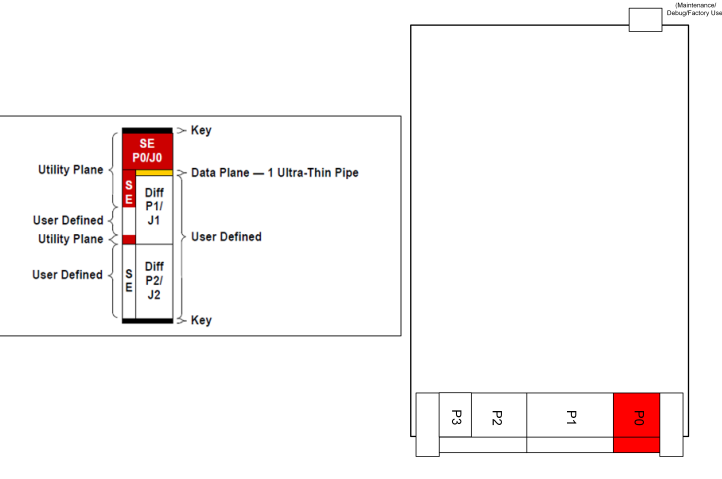
Rear I/O Data/Control Planes (P1)
The 68PW1 has the configuration option for specifying a high-speed serial interface fabric bus connection - PCIe ver. 2.0 (x1). As defined in the OpenVPX bridge or payload slot specifications, the 68PW1 requires only one ‘ultra-thin pipe' (one Tx and one Rx differential pair), which provides additional user I/O definition opportunity. Additionally, the 68PW1 can be commanded/controlled via single port Gig-E (option for 1000Base-KX interface). Additional I/O is also defined on the P1 user defined plane. Signals defined as N/C currently have no functionality associated or are considered optional and are not required for general operation.
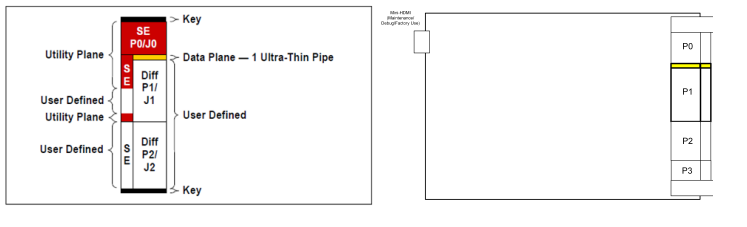
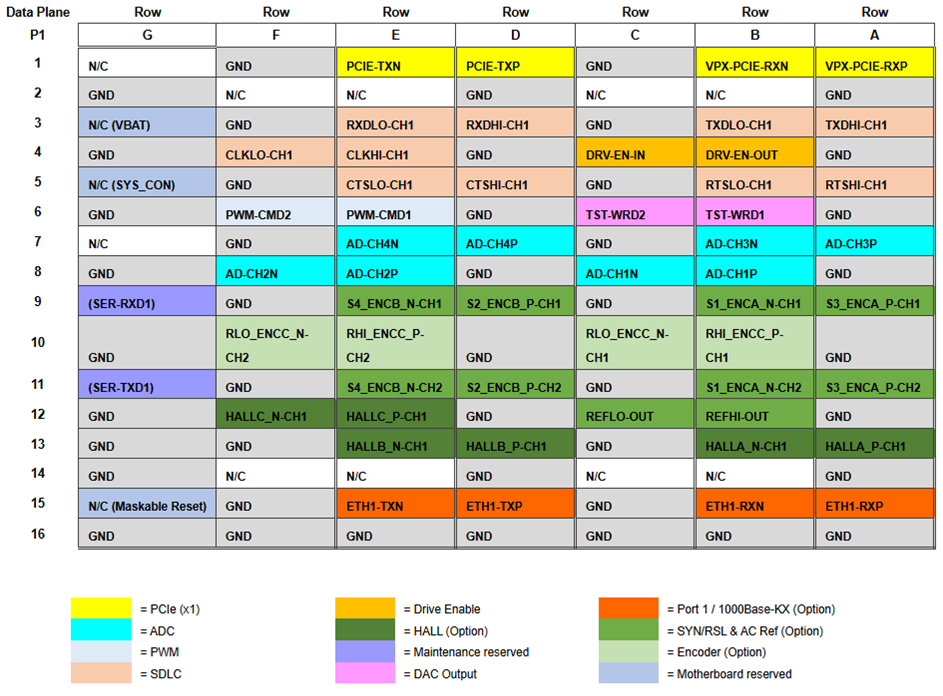
APPENDIX: 68PW1 FAULT LOG
Description
The fault logging system in the PWM card will store, in non-volatile memory, the board’s condition, e.g. current, voltage, and temperature at the time of a fault.
Hardware
The NVM device (FM24CL64B) is a ferroelectric RAM with 64-Kbit of storage, organized as 8K x 8. Each RAM entry is 8 bits wide. There is a total of 8K cells. The FRAM is written and read over an i2c bus.
Logging Information
The following table shows the information that will be logged at the time of a fault. SW will poll the C_ADDR_FAULT_EVENT_FLAG register every 100ms to capture a fault.
Information Logged |
Data Bytes |
Description |
ETC |
4 |
The ETC stores the elapsed time in a non-volatile 32- bit register with quarter second resolution. It can accumulate 298,261 hours, or about 34 years of time. Once the elapsed time register reaches 0xFFFFFFFF, counting stops. It does not roll over. This information is used to differentiate fault events |
Status Register |
2 |
The status register gives real-time monitoring of fault bits |
Latched Status Register |
2 |
Register used to store which status bits tripped during operation |
PS Voltage |
2 |
Measurement of the 65V power supply voltage. |
PS Current |
2 |
Measurement of the 65V power supply current. |
PS BB1 Temp |
2 |
Measurement of the 65V power supply temperature. |
PS BB2 Temp |
2 |
Measurement of the 65V power supply temperature. |
Drive 1 Voltage |
2 |
Measurement of the drive voltage. |
Drive 2 Voltage |
2 |
Measurement of the drive voltage. |
Drive 1 Current |
2 |
Measurement of the drive current. |
Drive 2 Current |
2 |
Measurement of the drive current. |
Drive Temperature |
2 |
Measurement of the drive temperature. |
26 Bytes of data is written to the NVM during a fault. The size of the NVM device determines how many events can be stored.
A total of 150 Fault Events can be stored in NVM at once time. The total number of fault events currently logged is also stored in NVM. Once at full capacity, new entries will overwrite the oldest entries.
Fault Log Access (FPGA REGION = USER INTERFACE)#
The access interface is comprised of two parts: a data register and a control register.
Register |
Description |
Data Register (RO) |
Once a request for a fault event is made, data from NVM is written to this register. |
Control Register (R/W) |
Raytheon will request to read a specific event from NVM by writing to this register. The MSB of this register is defined as a request for event bit. Bits [9:0] represent the event that is being requested. Writing all 0’s to bits [9:0] will return the event count (number of faults that occurred) in the data register. The event count will always point to the most recent event. The event count will not exceed 150. Once a count of 150 is read, it is known that the most recent event will always be at 150. After a request, the MSB of the control reg. will be cleared by the PWM card to signify that the data in the data reg. is valid. The following write commands are valid: x8000 = Return event count x8001 - x8096= Return data of specified event (1-150). xF000 = CLEAR FAULT LOG. |
*Requesting an event that has not occurred will result NO NEW DATA. The MSB of the control register will be cleared, but the data register will not be written to.
**Requesting the same event more than 13 times will continue to return data word 13 of that event.
***Clearing the fault log will reset the event count to 0 by writing all zeros to the “Fault Logging Region “of the NVM.
Example Data Retrieval Scenario (User Side)
The following steps detail the method to retrieve the most recent fault event from NVM.
-
Write x8000 to the Fault Log Control Register to get the event count.
-
Read the Fault Log Control Register to ensure the MSB is cleared, indicating the data in the Fault Log Data Register is valid.
-
Read the Fault Log Data Register to retrieve the Event Count. In this example assume the Event Count is 2. The Data Register will read 0x0002.
-
Write to the Control Register x”8002” to begin data acquisition of event #2.
-
Read the Control Register to ensure MSB is cleared. Expected read is x0002.
-
Read the Data Register to get a word of Event #2.
-
Repeat step 4-6 eleven more times to read the FULL fault event.
The following table details how to parse and transform the data from the data register into meaningful information.
S T A R T of E V E N T |
|||
Word of an Event |
Data Register Contents |
Data Translation |
Definition |
1 |
0002 |
Data 1 and Data 2 of an event represent the ETC register. Data 1 is the high word, while data 2 is the low word. Concatenate data 2 to data 1 to retrieve the 32-bit ETC value in Hex. 0002_5020h = 151584_dec Total Elapsed Time 151584 * 0.25 sec = 37896 seconds |
Elapsed Time (ETC) |
2 |
5020 |
Data 1 and Data 2 of an event represent the ETC register. Data 1 is the high word, while data 2 is the low word. Concatenate data 2 to data 1 to retrieve the 32-bit ETC value in Hex. 0002_5020h = 151584_dec Total Elapsed Time 151584 * 0.25 sec = 37896 seconds |
Elapsed Time (ETC) |
3 |
2200 |
- Drive Fault - Drive Overcurrent |
Status Register |
4 |
A214 |
- Master Drive - Drive Fault - Drive Overcurrent - PS Over Temp - Drive Over Temp |
Latched Status Reg. |
5 |
0976 |
0976h = 2422_dec = 50.49157 Volts |
PS Voltage |
6 |
005D |
005Dh = 93_dec = 1.498535 A |
PS Current |
7 |
0072 |
0072h = 114_dec = 114 C |
PS BB1 Temp |
8 |
FFDC |
FFDCh = -36_dec = - 36 C |
PS BB2 Temp |
9 |
289C |
298Ch = 10396_dec = 47.630625 Volts |
Drive 1 Voltage |
10 |
08BC |
08BCh = 2236_dec = 11.25877 Volts |
Drive 2 Voltage |
11 |
A9DC |
A9DCh = -22052_dec = -27.130907 Amps |
Drive 1 Current |
12 |
267B |
276Bh = 9851_dec = 12.119833 Amps |
Drive 2 Current |
13 |
0000 |
0000h = 0 C |
Drive Temperature |
E N D of E V E N T |
|||
Revision History
Motherboard Manual - 68PW1 Revision History
Revision |
Revision Date |
Description |
C |
2023-03-09 |
ECO C10038, initial release of 68PW1 manual. |
C1 |
2024-05-20 |
ECO C11549, pg.6, updated block diagram. Pg.6, updated Ancillary I/O bullet (changed 2x A/D to 4x). Pg.6, updated Front/Maintenance I/O bullet (changed 2 D/A to 3 D/A). Pg.7, updated A/D spec(changed 2x A/D to 4x). Pg.7, updated D/A (changed 2 D/A to 3 D/A). Removed ZynqCore/Aux/DDR Voltage register descriptions from Motherboard Monitoring Registers. Pg.24,updated MB Sensor Summary Status register to add PS references; updated Bit table to change voltage/current bits to 'reserved'. Pg.24, updated MB/PS Sensor Registers description to better describe register functionality and to add figure. Pg.25, added 'Exceeded' to threshold bit descriptions. Pg.25-26, removed voltage/current references from sensor descriptions. Pg.30,removed Zynq Core/Aux/DDR Voltage register offsets. Pg.32, updated MB Health MonitoringRegisters offset tables. |
NAI Cares
Edit this on GitLab
North Atlantic Industries (NAI) is a leading independent supplier of Embedded I/O Boards, Single Board Computers, Rugged Power Supplies, Embedded Systems and Motion Simulation and Measurement Instruments for the Military, Aerospace and Industrial Industries. We accelerate our clients’ time-to-mission with a unique approach based on a Configurable Open Systems Architecture™ (COSA®) that delivers the best of both worlds: custom solutions from standard COTS components.
We have built a reputation by listening to our customers, understanding their needs, and designing, testing and delivering board and system-level products for their most demanding air, land and sea requirements. If you have any applications or questions regarding the use of our products, please contact us for an expedient solution.
Please visit us at: www.naii.com or select one of the following for immediate assistance: